You rely on connectors every time you interact with modern electronics. Pin Connector Types form the backbone of reliable signal transmission and power delivery. The global pin header connectors market reached USD 2.1 billion in 2023, with projections of USD 3.8 billion by 2032 and a 6.5% CAGR.
- Connectors support device miniaturization and complexity.
- M8 connector and Type B connector improve speed and current capacity.
- Connector factory innovations address bandwidth, pin count, and durability.
You see connectors in every device, from consumer gadgets to industrial systems. Manufacturers design connectors to meet specific needs, ensuring performance and resilience in demanding environments.
Understanding Pin Connectors
Definition and Function of Pin Connectors
Basic Structure of Pin Connectors
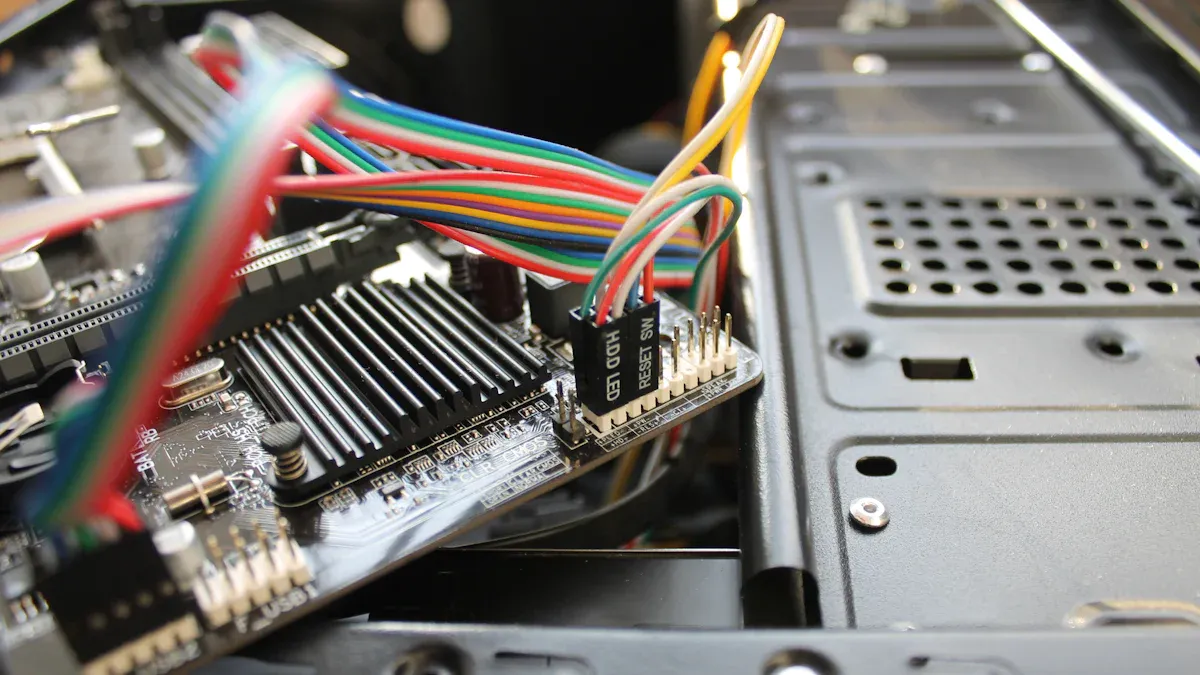
You encounter pin connectors in almost every electronic device you use. These components consist of metal pins arranged in a specific pattern, housed within an insulating material. The structure allows you to create secure electrical connections between circuit boards, wires, or modules. Manufacturers design pin connectors with features that support both ease of installation and long-term reliability.
Tip: Always check the pin arrangement and housing type before selecting a connector for your project. This ensures compatibility and prevents costly mistakes.
The technical standards for pin connectors highlight several essential functions. The table below summarizes these functions and their impact on electronic circuits:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of Pins | Determines the number of electrical pathways available, affecting the number of signals or power connections. |
| Pitch Arrangement | Refers to the distance between pins, crucial for compatibility and performance, especially in high-speed applications. |
| Pin Numbering | A standardized system for identifying pins, preventing misalignment that could disrupt systems. |
| Keying | A physical safeguard ensuring connectors are inserted correctly, preventing electrical shorts or damage. |
| Pin Sequencing | Determines the order of pin contact, important for stable power and ground connections. |
| Mounting Types | Refers to how connectors are attached to devices, affecting installation and usage. |
Electrical Role in Circuits
Pin connectors serve as the bridge for transmission of electrical signals and power. You rely on them to maintain stable transmission between different parts of a circuit. The arrangement and quality of the pins directly influence the efficiency of transmission. When you use high-quality pin connectors, you reduce the risk of signal loss and ensure consistent transmission. The design of these connectors supports both analog and digital transmission, making them versatile for various applications.
Importance of Pin Connectors in Electronic Systems
Signal Transmission Applications
Pin connectors play a vital role in transmission of data and control signals. You see them in devices where rapid transmission is essential, such as computers, smartphones, and industrial controllers. The precise alignment and secure contact points in pin connectors guarantee uninterrupted transmission. You benefit from reduced interference and improved transmission speed, which are critical for modern electronics.
Power Delivery Applications
You depend on pin connectors for safe and efficient transmission of electrical power. These connectors separate power, signal, and ground paths, which enhances safety and reliability. The inclusion of ground pins protects you from electric shock and supports stable transmission of power. Insulated housings and locking mechanisms prevent accidental disconnection, ensuring continuous transmission even in demanding environments.
- Pin connectors support both power and data transmission, enabling smart control and monitoring in devices.
- Their design makes installation and maintenance straightforward, saving you time and reducing repair costs.
- Durable materials allow pin connectors to withstand harsh conditions, maintaining reliable transmission over time.
Categories of Pin Connector Types

Understanding pin connector types helps you select the right solution for your electronic projects. You encounter a wide range of connectors, each designed for specific applications and environments. The following sections break down the main categories based on physical form, termination method, and pin count or pitch.
Pin Connector Types by Physical Form
Single-row vs. Double-row Pin Connectors
You often see single-row pin connector types in simple circuits. These connectors feature pins arranged in a straight line, making them easy to use for breadboards, prototyping, and basic connections. A 2 pin connector in a single-row format works well for straightforward power or signal links.
Double-row pin connector types provide two parallel lines of pins. You use these when you need to increase the number of connections without expanding the connector’s footprint. Double-row connectors appear in microcontroller boards, communication modules, and compact devices. When you need to connect multiple signals or power lines, double-row connectors offer a space-saving solution.
Circular vs. Rectangular Pin Connectors
Circular connectors stand out for their robust design and secure locking mechanisms. You find 5-pin connectors in circular form in industrial automation, medical devices, and transportation systems. The M5, M8, and M12 circular connectors serve different roles:
| Connector Type | Typical Applications |
|---|---|
| M5 Circular Connectors | Transportation and control systems, automated doors & ramps, sensor connectivity, data & communication devices |
| M8 Circular Connectors | Medical devices, ruggedized data loggers & sensors, electronic gauges & metering, avionics, marine electronics |
| M12 Circular Connectors | Industrial controls and automation, remote process sensors, robotics control systems, ruggedized networking, power conditioning systems |
Rectangular pin connector types dominate consumer electronics and computing. You see them in pin header connector arrays, sockets, and edge connectors. These connectors support high-density layouts and easy integration onto printed circuit boards. A 2 pin connector in rectangular form often appears in battery packs, LED strips, and small appliances.
Board-to-board Pin Connectors
Board-to-board connectors allow you to stack or align two printed circuit boards. You use these pin connector types in modular designs, embedded systems, and compact electronics. A 2 pin connector in this category provides a simple bridge for power or signal between boards. Multi-pin connectors in board-to-board formats enable complex data and power routing in laptops, tablets, and industrial controllers.
Wire-to-board Pin Connectors
Wire-to-board connectors let you attach individual wires to a circuit board. You rely on these connectors for flexibility in wiring harnesses, power supplies, and sensor modules. A 2 pin connector in this form is common in fan connections, battery leads, and small motors. 5-pin connectors in wire-to-board configurations support more complex signals or power needs, such as in robotics or automation panels.
Wire-to-wire Pin Connectors
Wire-to-wire connectors join two or more wires directly. You use these pin connector types in automotive wiring, lighting systems, and field repairs. A 2 pin connector in wire-to-wire form is ideal for quick splicing or extending cables. 5-pin connectors in this category handle multi-signal or multi-power connections, such as in sensor arrays or distributed control systems.
Note: You can choose between male and female pin connectors for all these physical forms. This ensures compatibility and secure mating in your assemblies.
Pin Connector Types by Termination Method
Soldered Pin Connectors
Soldered pin connector types require you to attach wires or pins using solder. This method creates a strong, permanent bond. You often use soldered 2 pin connector types in low-volume, high-density applications where reliability matters most. Soldering works well for custom projects, repairs, and prototypes.
Crimped Pin Connectors
Crimped connectors use a mechanical process to attach wires to pins. You insert the wire into a metal barrel and compress it with a crimping tool. Crimped 2 pin connector types excel in mass production because they are fast and cost-effective. You find crimped 5-pin connectors in automotive harnesses, appliances, and industrial equipment.
- Choosing the correct contact termination type is essential for ensuring a reliable and secure connection.
- Crimping is cost-effective for mass production, while soldering is better for low-volume, high-density connectors.
Press-fit Pin Connectors
Press-fit connectors use force to insert pins into plated holes on a circuit board. You do not need solder or crimping tools. This method provides strong mechanical retention and reliable electrical contact. Press-fit 2 pin connector types are common in high-reliability applications, such as telecommunications and automotive control units.
IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) Pin Connectors
IDC pin connector types allow you to connect wires without stripping insulation. You press the wire into a slot, and the connector pierces the insulation to make contact. IDC 2 pin connector types are ideal for ribbon cables, quick assembly, and automation. 5-pin connectors in IDC form support multi-wire connections in printers, computers, and industrial controls.
- Connectors allow for quick connection and disconnection without altering the cable.
- They are ideal for applications requiring frequent reconfiguration, troubleshooting, or equipment upgrades.
Tip: Automation needs may favor crimping or IDC for high-volume production. Clamp terminations work best in high-vibration environments.
Pin Connector Types by Pin Count and Pitch
Low-pin-count Pin Connectors
Low-pin-count pin connector types, such as the 2 pin connector, serve simple circuits. You use these connectors for power, ground, or basic signal transmission. Single pin connectors and 2 pin connector types appear in LED projects, battery connections, and hobby electronics.
| Connector Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Single Pin Connectors | Basic form ideal for small-scale circuits and prototyping. | LED projects, battery connections, hobby electronics |
| Multi-Pin Connectors | Designed for multiple connections in a single housing. | Communication equipment, power distribution systems |
| 10-Pin Connectors | Popular in industrial applications and microcontroller-based systems. | Industrial applications, microcontroller systems |
- Smaller pitch allows for more compact designs, which is beneficial in space-constrained applications.
- Smaller pin sizes generally lead to lower current-carrying capacity, which must meet application requirements.
High-density Pin Connectors
High-density pin connector types pack many pins into a small area. You use these connectors in advanced electronics, such as smartphones, laptops, and industrial controllers. 5-pin connectors in high-density layouts support complex data and power needs. When you need to save space but maintain functionality, high-density connectors provide the solution.
- Larger pitch enhances manufacturability and reliability, but may not fit in compact designs.
Note: Always match the pin count and pitch to your application’s electrical and mechanical requirements. This ensures safe operation and long-term reliability.
You also encounter specialized connectors like the screw terminal connector and blade connector in power distribution and control panels. These connectors offer robust mechanical connections and easy maintenance.
You see 5-pin connectors in almost every industry. 5-pin connectors appear in board-to-board, wire-to-board, and wire-to-wire forms. 5-pin connectors support both signal and power transmission. 5-pin connectors provide flexibility for modular designs. 5-pin connectors offer secure connections in harsh environments. 5-pin connectors enable rapid assembly and maintenance. 5-pin connectors reduce wiring complexity. 5-pin connectors improve system reliability. 5-pin connectors are compatible with male and female pin connectors. 5-pin connectors are available in crimped, soldered, and IDC forms. 5-pin connectors support high-density layouts. 5-pin connectors are used in sensor arrays. 5-pin connectors are found in automation systems. 5-pin connectors are common in robotics. 5-pin connectors are essential for distributed control. 5-pin connectors simplify troubleshooting. 5-pin connectors are easy to replace. 5-pin connectors are cost-effective for mass production. 5-pin connectors are suitable for high-vibration environments. 5-pin connectors are resistant to corrosion. 5-pin connectors are available in gold-plated versions. 5-pin connectors are compatible with standard housings. 5-pin connectors are available in custom configurations. 5-pin connectors are used in medical devices. 5-pin connectors are found in avionics. 5-pin connectors are used in marine electronics. 5-pin connectors are suitable for ruggedized networking. 5-pin connectors are used in power conditioning systems. 5-pin connectors are found in remote process sensors. 5-pin connectors are used in robotics control systems. 5-pin connectors are available in press-fit forms. 5-pin connectors are used in communication devices. 5-pin connectors are found in data loggers. 5-pin connectors are used in metering equipment. 5-pin connectors are used in electronic gauges. 5-pin connectors are found in transportation systems. 5-pin connectors are used in control panels. 5-pin connectors are available in both male and female pin connectors. 5-pin connectors are used in modular assemblies. 5-pin connectors are found in field repairs. 5-pin connectors are used in lighting systems. 5-pin connectors are available in both circular and rectangular forms. 5-pin connectors are used in battery packs. 5-pin connectors are found in LED strips. 5-pin connectors are used in small appliances. 5-pin connectors are used in fan connections. 5-pin connectors are found in battery leads. 5-pin connectors are used in small motors. 5-pin connectors are used in sensor modules. 5-pin connectors are found in wiring harnesses. 5-pin connectors are used in power supplies. 5-pin connectors are used in quick splicing. 5-pin connectors are found in extending cables. 5-pin connectors are used in distributed control systems. 5-pin connectors are found in sensor arrays. 5-pin connectors are used in automation panels. 5-pin connectors are found in robotics. 5-pin connectors are used in industrial controls. 5-pin connectors are found in printers. 5-pin connectors are used in computers. 5-pin connectors are found in industrial controllers. 5-pin connectors are used in laptops. 5-pin connectors are found in tablets. 5-pin connectors are used in microcontroller boards. 5-pin connectors are found in communication modules. 5-pin connectors are used in compact devices. 5-pin connectors are found in embedded systems. 5-pin connectors are used in modular designs. 5-pin connectors are found in consumer electronics. 5-pin connectors are used in computing. 5-pin connectors are found in pin header connector arrays. 5-pin connectors are used in sockets. 5-pin connectors are found in edge connectors. 5-pin connectors are used in printed circuit boards. 5-pin connectors are found in high-density layouts. 5-pin connectors are used in easy integration. 5-pin connectors are found in power or signal links. 5-pin connectors are used in straightforward connections. 5-pin connectors are found in breadboards. 5-pin connectors are used in prototyping. 5-pin connectors are found in basic connections. 5-pin connectors are used in simple circuits. 5-pin connectors are found in small-scale circuits. 5-pin connectors are used in prototyping. 5-pin connectors are found in hobby electronics. 5-pin connectors are used in communication equipment. 5-pin connectors are found in power distribution systems. 5-pin connectors are used in industrial applications. 5-pin connectors are found in microcontroller systems.
Specialized Pin Connector Types
Spring-loaded (Pogo Pin) Connectors
You encounter spring-loaded connectors, often called pogo pin connectors, in devices that require frequent connection and disconnection. These connectors use a spring mechanism inside each pin, which maintains consistent contact pressure. You benefit from reliable electrical performance, even when the device moves or vibrates.
Pogo pin connectors excel in test equipment, docking stations, and modular consumer electronics. You use them for battery charging, signal transmission, and temporary connections. Their design supports high mating cycles, so you can connect and disconnect thousands of times without losing reliability.
Tip: Choose pogo pin connectors for applications where durability and repeated use matter most.
You see these connectors in compact devices, where space is limited. Their small size fits modern electronics, and their robust construction withstands harsh environments. You rely on pogo pin connectors for versatility in signal and power transmission, supporting both high and low-frequency signals.
Gold-plated Pin Connectors
Gold-plated pin connectors offer superior conductivity and corrosion resistance. You select these connectors when you need stable signal transmission and long-term reliability. Gold plating reduces contact resistance, which improves performance in high-speed data and sensitive analog circuits.
You find gold-plated connectors in medical devices, aerospace systems, and high-end consumer electronics. These connectors maintain signal integrity, even in environments with moisture or contaminants. You benefit from enhanced EMI resistance and waterproof performance, which protects your devices from interference and damage.
- Gold-plated connectors support both power and signal transmission.
- You use them in harsh environments, including automotive and industrial applications.
| Connector Type | Unique Features/Advantages |
|---|---|
| Gold-plated Pin Connectors | Low contact resistance, high durability, excellent corrosion protection, reliable in extreme conditions |
Note: Gold-plated connectors cost more than standard connectors, but you gain improved reliability and longer service life.
Custom and Proprietary Pin Connectors
You encounter custom and proprietary pin connectors in specialized equipment and branded devices. Manufacturers design these connectors to meet unique requirements, such as unusual pin counts, shapes, or locking mechanisms. You use custom connectors in robotics, advanced medical systems, and high-density computing.
Custom connectors allow you to optimize space, improve safety, and enhance performance. You benefit from features like keyed housings, waterproof seals, and integrated testing points. These connectors fit tight spaces and withstand frequent plugging and unplugging.
- You see custom connectors in modular assemblies, sensor arrays, and distributed control systems.
- Proprietary connectors often include advanced features, such as quick-connect mechanisms and precision alignment.
| Connector Type | Unique Features/Advantages |
|---|---|
| SC (Subscriber Connector) | Square shape prevents rotation, reliable for network installations, clicks firmly into place |
| LC (Lucent Connector) | Smaller size for high-density applications, distinctive latch mechanism for secure connection |
| ST (Straight Tip) | Bayonet-style lock for secure connection, durable for frequent use |
| MTP/MPO (Multi-fiber Push-On) | Joins multiple fibers at once, precision design maintains signal quality |
| DIN Connectors | Various pin counts, sturdy design for frequent plugging/unplugging |
| M12 Connectors | Water-resistant, quick-connect features, used in sensors and actuators |
| Circular Connectors | Round design for tight seals, suitable for heavy-duty applications |
| Terminal Blocks | Simple wire connections without soldering, includes testing points for organization |
You gain versatility, compact form factor, and enhanced reliability when you choose specialized pin connector types. These connectors support modern device miniaturization and perform reliably in demanding environments.
Applications of Pin Connectors in Modern Electronics

Pin Connector Applications in Consumer Electronics
Smartphones and Tablets
You interact with pin connectors every time you charge your smartphone or transfer data between devices. These connectors enable seamless connection for power banks, wireless chargers, and phone cases. You rely on efficient data transmission and stable power delivery in these applications. Manufacturers design connectors to support high-speed data transfer and robust connection, which ensures your devices operate reliably.
- You find pin connectors in:
- Charging ports for rapid power delivery
- Internal connections for camera modules and sensors
- Data synchronization interfaces for accessories
Laptops and PCs
Pin connectors play a vital role in laptops and PCs. You use them for connecting hard drives, memory modules, and peripheral devices. These connectors support high-density data transmission and maintain secure connection in compact spaces. You benefit from reliable connectivity for USB ports, audio jacks, and display interfaces. The design of these connectors allows for easy upgrades and repairs, which extends the lifespan of your devices.
- Common applications include:
- Internal data buses for memory and storage
- Connection points for cooling fans and batteries
- Interfaces for external devices such as printers and monitors
Wearables
Wearable technology depends on miniature pin connectors for charging and data synchronization. You experience fast and reliable connection in smartwatches and fitness bands. These connectors support efficient data exchange between your wearable and smartphone. You also benefit from robust connection that withstands movement and daily wear.
Key applications in consumer electronics:
- Smartphones and accessories
- Smart wearables
- Home audio-visual systems
Tip: You should choose connectors with high mating cycles for wearables to ensure long-term reliability.
Pin Connector Applications in Automotive Industry
Engine Control Units
You rely on pin connectors to link sensors and controls within engine control units. These connectors handle high power and maintain stable data transmission in harsh environments. You benefit from water and dust resistance, which ensures reliable connection in complex automotive applications.
Infotainment Systems
Pin connectors support data and power transmission in infotainment systems. You experience seamless connection for audio, video, and navigation modules. These connectors meet international standards for safety and reliability, which guarantees consistent performance.
Sensor Connections
You depend on pin connectors for sensor connections throughout your vehicle. These connectors provide secure connection for data exchange between sensors and control units. Manufacturers follow strict guidelines for design and manufacturing, which ensures products meet industry requirements for durability and safety.
- Automotive applications require:
- Water and dust-resistant connectors
- High-power handling capability
- Compliance with international standards
Pin Connector Applications in Industrial Equipment
Automation Systems
You see pin connectors in industrial automation applications, where they provide flexible wiring solutions. Wire-to-board connectors adapt to changing system requirements and ensure stable data and power transmission. You rely on these connectors for communication between controllers, sensors, and actuators.
Robotics
Industrial robots utilize small, robust connectors for essential data and power transmission. You benefit from reliable connection in automated environments, which supports precise control and rapid data exchange. Autonomous delivery robots also require dependable connectors to function effectively in both industrial and residential settings.
Control Panels
Pin connectors facilitate the transmission of control signals and power in control panels. You use these connectors to maintain stable connection between robots, sensors, and other equipment. The shift from traditional fieldbus technologies to industrial Ethernet highlights the need for advanced connectors that support higher speeds and bandwidths. You achieve robust supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems with extensive networks of connectors and cabling, which maintain low latency and high redundancy in time-sensitive applications.
| Industrial Automation Applications | Role of Pin Connectors |
|---|---|
| Automation Systems | Flexible wiring, stable data transmission |
| Robotics | Reliable connection, essential for operation |
| Control Panels | Control signal and power transmission |
Note: You should select connectors designed for industrial automation applications to ensure reliable data and power connection in demanding environments.
Pin Connector Applications in Medical Devices
Diagnostic Equipment
You depend on pin connectors for reliable performance in medical diagnostic equipment. These applications require connectors that meet strict safety and reliability standards. In diagnostic imaging machines, laboratory analyzers, and portable ultrasound devices, pin connectors provide stable signal and power transmission. You see hybrid connectors in these medical applications, which reduce cable entanglement and stress. This design improves both reliability and safety. When you use a single connector for multiple functions, you minimize potential points of failure. Misconnections can lead to serious patient injuries, so you must select pin connectors with secure mating features.
Medical devices must comply with IEC 60601-1 and ISO standards. These standards require extended creepage and clearance distances, which most commodity connectors cannot meet. The FDA classifies medical devices into three classes based on risk, influencing your connector selection. The table below summarizes insulation requirements for different medical device types:
| Device Type | Insulation Voltage | Creepage Distance | Clearance Distance | Insulation Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type B | 1,500 Vac | 2.5 mm | 2.0 mm | Basic insulation |
| Type BF | 3,000 Vac | 5 mm | 4.0 mm | Double insulation |
| Type CF | 4,000 Vac | 8 mm | 5.0 mm | Double insulation |
You must ensure that pin connectors in medical diagnostic applications meet these requirements to protect patients and operators.
Patient Monitoring Systems
You rely on pin connectors in patient monitoring systems for continuous and accurate data transmission. These applications include ECG monitors, pulse oximeters, and wearable health trackers. Pin connectors in these medical devices must withstand frequent connection cycles and resist accidental disconnection. You benefit from hybrid connectors, which simplify maintenance and reduce the risk of misconnections. Medical applications demand connectors with robust insulation and secure locking mechanisms. You must verify that each connector meets the required insulation and spacing standards to ensure patient safety.
Note: Always check that your pin connectors comply with medical regulations before integrating them into any application.
Pin Connector Applications in Aerospace and Defense
Avionics Systems
You encounter pin connectors in avionics systems, where they ensure reliable data transmission and power distribution. These applications include flight control, navigation, and power management. Pin connectors in aerospace must withstand vibrations, mechanical shocks, and extreme temperatures ranging from -65°C to +200°C. You select connectors with enhanced shielding and corrosion resistance for these demanding environments.
Communication Systems
You use pin connectors in communication systems for in-flight entertainment, satellite links, and secure military communications. These applications require high-speed data transmission and lightweight, compact designs. Pin connectors must provide EMI shielding to prevent disruption of critical systems. You must choose connectors that comply with aerospace standards to guarantee safety and performance.
- Key performance criteria for aerospace and defense applications:
- High reliability and durability
- Resistance to corrosion and environmental factors
- Lightweight and compact construction
- Effective EMI shielding
Pin Connector Applications in Other Technologies
Test and Measurement Equipment
You rely on pin connectors in test and measurement equipment for accurate signal transmission and repeatable connections. These applications include oscilloscopes, signal analyzers, and calibration devices. Pin connectors must support frequent mating cycles and maintain low contact resistance. You benefit from connectors designed for easy handling and secure locking, which ensures consistent results in every application.
Emerging Technologies (IoT Devices, Electric Vehicles, Renewable Energy Systems)
You see pin connectors driving innovation in emerging technologies. In IoT devices, you use compact connectors for sensor networks and smart home applications. Electric vehicles require pin connectors that handle high currents and provide robust insulation. Renewable energy systems depend on pin connectors for reliable power transmission in solar panels and wind turbines. These applications demand connectors that combine durability, safety, and ease of installation.
Tip: Select pin connectors rated for your specific application to maximize safety and performance in all modern technologies.
Key Specifications and Standards for Pin Connectors
Electrical Ratings for Pin Connectors
Voltage Specifications
You must always consider voltage ratings when selecting pin connectors for your projects. The maximum voltage rating tells you how much voltage a connector can handle before risking flashover or insulation breakdown. The working voltage rating, recommended by manufacturers, helps you match the connector to your system’s needs. If you exceed these ratings, you risk damaging your equipment or causing unsafe conditions. Pin connectors with proper voltage ratings ensure safe operation in both consumer and industrial electronics.
Current Specifications
Current ratings are just as important as voltage. The rated current defines how much electrical load a connector can carry without overheating. You need to control temperature rise within the connector to maintain high-performance and prevent failures. Pin connectors with higher current ratings support demanding applications, such as power supplies and motor controls. Always check the rated current to avoid excessive heat and ensure reliable operation.
Tip: Always match the voltage and current ratings of your pin connectors to your application’s requirements for optimal safety and performance.
Mechanical Properties of Pin Connectors
Durability and Robustness
You rely on connectors to withstand tough environments. High-performance pin connectors must resist vibration, temperature extremes, and moisture. Manufacturers test these properties using vibration tests, thermal cycling, and sealing assessments. The table below summarizes key mechanical properties and how they are measured:
| Mechanical Property | Importance in Demanding Environments | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration Resistance | Prevents damage in high-vibration settings | Sine and random vibration testing |
| Temperature Stability | Ensures function under extreme temperatures | Thermal cycling tests |
| Sealing Capabilities | Protects against moisture and contaminants | IEC IP67 and IP69K sealing tests |
You benefit from anti-vibration features, strong covers, and stiffening ribs. These design elements help pin connectors maintain high-performance in automotive, aerospace, and industrial systems.
Mating Cycles and Longevity
The number of mating cycles measures how many times you can connect and disconnect a connector before it wears out. High-performance pin connectors offer thousands of cycles, making them ideal for applications that require frequent maintenance or reconfiguration. You should always check the rated mating cycles to ensure long-term reliability in your devices.
Material Considerations for Pin Connectors
Contact Materials (Copper, Gold, Tin)
The choice of contact material directly affects the performance and cost of pin connectors. You often see copper alloys like brass and phosphor bronze used for their good conductivity and mechanical strength. For high-performance applications, manufacturers use beryllium copper or apply gold plating to reduce contact resistance and improve corrosion resistance. The table below compares common materials:
| Material | Properties | Performance Influence | Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Good conductivity, workability | Cost-effective, may need coating | Low cost |
| Bronze | High strength, corrosion resistance | Good for mechanical stress | Moderate cost |
| Phosphor Bronze | Wear resistance, elasticity | Excellent for high-cycling environments | Moderate cost |
| Beryllium Copper | High conductivity, strength, corrosion resistance | Ideal for precision, frequent connections | Higher cost |
| Gold Plating | Low contact resistance, corrosion resistance | Critical for stable signals in high-performance uses | Expensive, thin layers |
| Silver Plating | Best conductivity, less oxidation resistance | Used for high conductivity needs | Moderate cost |
| Palladium Plating | High corrosion resistance | Durable for industrial environments | Higher cost |
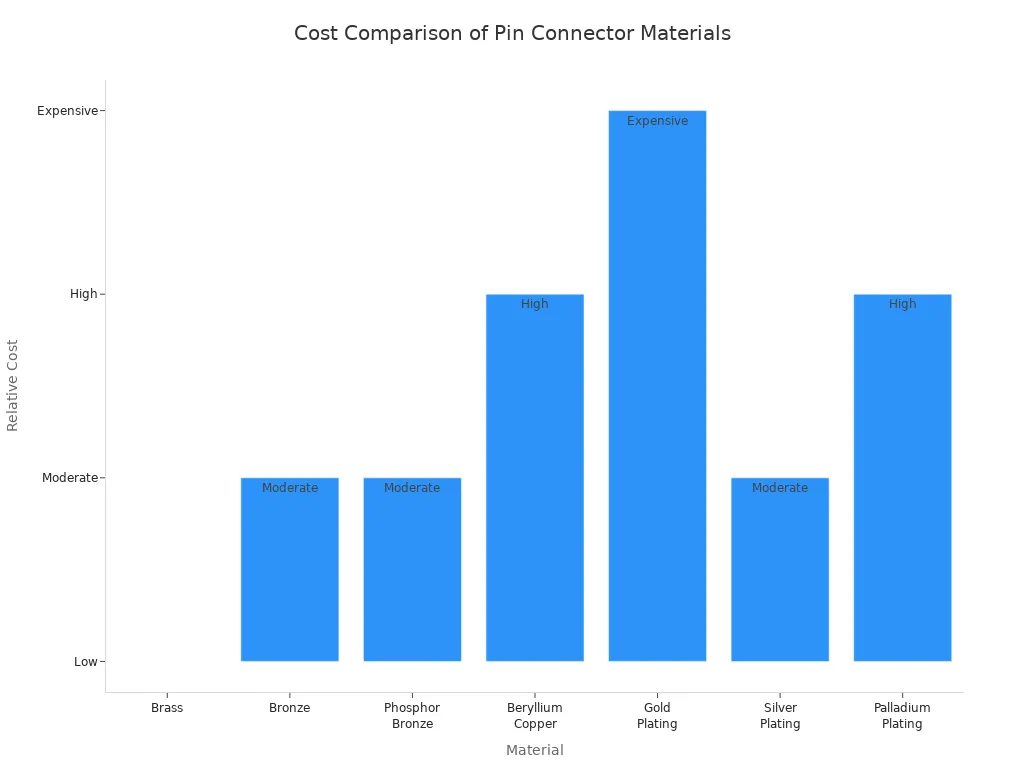
You should select contact materials based on your application’s electrical, mechanical, and environmental requirements. High-performance pin connectors often use precious metal coatings for maximum reliability.
Housing Materials (Plastic, Metal)
The housing protects the contacts and ensures mechanical stability. You find engineering plastics like nylon and polycarbonate in many connectors. These materials offer lightweight construction and good resistance to chemicals. For rugged or high-performance environments, manufacturers use metals such as aluminum or stainless steel. Metal housings provide extra strength and shield against electromagnetic interference. Your choice of housing material affects weight, durability, and cost.
Note: Always balance performance, durability, and budget when choosing materials for pin connectors. The right combination ensures your connectors deliver high-performance in every application.
Environmental Factors Affecting Pin Connectors
Temperature Range
You must consider temperature range when selecting pin connectors for electronic systems. Temperature directly affects the performance and longevity of connectors. High temperatures can degrade materials and increase electrical resistance. Low temperatures may cause brittleness, which affects connector integrity. You see material properties change as temperature fluctuates, which can lead to increased contact resistance and reduced reliability.
- Temperature and humidity alter material properties and electrical behavior.
- High temperatures degrade materials and increase electrical resistance.
- Low temperatures result in brittleness, affecting connector integrity.
You should always check the manufacturer’s standards for operating temperature. Standards specify the safe range for each connector type. You ensure compliance with these standards to prevent failures in harsh environments. You protect your devices by choosing connectors that meet the required standards for temperature resilience.
Moisture and Corrosion Resistance
Moisture and corrosion pose significant risks to pin connectors. High moisture levels accelerate oxidation and increase the risk of short circuits. Humidity can cause corrosion, which leads to electrical failures and increased contact resistance. Dry conditions may increase static electricity risks, which can damage sensitive components.
- Environmental factors such as humidity and temperature lead to corrosion and increased contact resistance.
- Material degradation occurs due to prolonged exposure to adverse conditions.
- Connectors are vulnerable to humidity, temperature, and vibration, which can shorten service life.
You must select connectors with moisture and corrosion resistance that meet industry standards. You look for compliance with standards that specify protective coatings and sealing features. You extend the lifespan of your electronic systems by ensuring compliance with moisture and corrosion resistance standards.
Industry Standards for Pin Connectors
IEC Standards for Connectors
You rely on IEC standards to ensure safety, compatibility, and performance in pin connectors. IEC 61076-4-101 is an international standard for 2 mm pitch HM connectors. You see these standards define connector dimensions, electrical ratings, and environmental requirements. You achieve compliance by selecting connectors certified to IEC standards. You benefit from global compatibility and reliable operation in diverse applications.
MIL-SPEC Standards for Connectors
You encounter MIL-SPEC standards in military and aerospace applications. MIL-C-83503 is a U.S. Department of Defense standard for flat cable connectors. You trust these standards to guarantee durability, vibration resistance, and environmental protection. You ensure compliance with MIL-SPEC standards for mission-critical systems. You select connectors that meet these standards to withstand extreme conditions and maintain performance.
RoHS Compliance for Pin Connectors
You must verify RoHS compliance when choosing pin connectors for modern electronics. RoHS compliance ensures connectors do not contain hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, or cadmium. You protect users and the environment by selecting connectors that meet RoHS compliance standards. You see manufacturers label connectors to indicate compliance with RoHS standards. You achieve regulatory compliance and support sustainable design by following these standards.
UL and CSA Certification Standards
You depend on UL and CSA certification standards for safety and reliability. UL and CSA standards specify requirements for electrical insulation, flammability, and mechanical strength. You ensure compliance by choosing connectors with UL and CSA certification marks. You avoid additional testing when using certified connectors in devices that meet safety standards. You meet local and international safety standards by selecting connectors with proper certification.
| Standard Name | Description |
|---|---|
| DIN 41612 | Defined by the German Institute for Standardization, specifying board-to-board connectors. |
| MIL-C-83503 | U.S. Department of Defense standard for flat cable connectors, commonly known as MIL connectors. |
| IEC 61076-4-101 | International standard for 2 mm pitch HM connectors. |
| USB | A communication standard that also specifies the connector design. |
Tip: You should always verify compliance with relevant standards before integrating pin connectors into your designs. You reduce risk and ensure long-term reliability by following industry standards.
You see safety standards prevent accidents and protect consumers from electric shock and fire hazards. Different countries have unique standards based on voltage and weather conditions. You achieve compliance with local and international standards by selecting certified connectors. You ensure compatibility and safety in every application by following these standards.
Selection of the Right Pin Connector Types
Assessing Application Requirements for Pin Connectors
Electrical Needs and Load
You must evaluate the electrical requirements before making any selection of pin connectors. Voltage and current ratings determine the safe operation of your electronic system. You need to match the connector’s specifications with the demands of your application. If you select a connector with insufficient ratings, you risk overheating and signal loss. You should also consider contact resistance, which affects both efficiency and reliability. High-quality connectors maintain low resistance and stable performance under load.
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Requirements | Considerations for the physical durability and fit of the connector in the application. |
| Electrical Requirements | Voltage, current, and contact specifications that the connector must meet. |
| Service Environment | Factors like temperature, exposure to substances, and mechanical stresses affecting the design. |
| Material Choices | Selection of materials that impact weight, cost, and reliability of the connector. |
| Space Requirements | Constraints on size and layout that must be accommodated in the design. |
| Termination Styles | Methods for connecting the connector to conductors, affecting sealing and mechanical strength. |
You should review these criteria during the selection process to ensure optimal reliability and interoperability.
Mechanical Constraints and Space
You need to assess the physical constraints of your design. Space limitations often dictate the size and shape of pin connectors. If you work with compact devices, you must select connectors that fit within tight layouts. Mechanical durability also plays a crucial role. You should choose connectors that withstand vibration, shock, and repeated use. The right selection ensures that your connectors remain secure and reliable throughout the product’s lifecycle.
Tip: Always verify the mounting style and footprint of each connector to avoid interference with other components.
Matching Pin Connector Types to Applications
Signal vs. Power Pin Connectors
You must distinguish between signal and power transmission when selecting pin connectors. Signal connectors require low contact resistance and shielding to prevent interference. Power connectors need higher current ratings and robust construction. You should select connectors based on the type of transmission in your application. If you mix signal and power lines, you risk compromising reliability and safety.
- Signal connectors support data transmission and require precise alignment.
- Power connectors deliver energy and must handle higher loads.
You should always match the connector type to the specific function in your system. This approach improves reliability and simplifies maintenance.
Environmental Demands and Protection
You must consider environmental factors during the selection process. Exposure to water, chemicals, and dust can degrade connectors and reduce reliability. You should select pin connectors with appropriate sealing and protective features. International standards, such as IEC 60309-2, specify layouts and protection levels for different environments. You need to verify compliance with these standards to ensure interoperability and long-term reliability.
- Resistance to moisture and chemicals extends the lifespan of connectors.
- Dust protection maintains signal integrity and prevents failures.
You should always review the service environment before finalizing your selection. This step helps you avoid costly replacements and downtime.
Note: Environmental demands often require specialized connectors with enhanced protection and durability.
Evaluating Reliability and Performance of Pin Connectors
Contact Quality and Plating
You must evaluate contact quality when selecting pin connectors. High-quality contacts reduce resistance and improve reliability. Gold plating offers superior conductivity and corrosion resistance. You should select connectors with appropriate plating for your application. If you use connectors in harsh environments, gold or palladium plating enhances reliability and longevity.
| Methodology | Description |
|---|---|
| Mathematical Modeling | Establishes a relationship between contact pair structure parameters and contact force using a cantilever beam model. |
| Accelerated Degradation Testing | Tests the reliability of multi-aperture electrical connectors under constant stress to assess performance degradation over time. |
| Statistical Analysis | Analyzes test data to verify the reliability models and assess the contact reliability of connectors. |
You should review these methods during the selection process to ensure that your connectors meet the required standards for reliability.
Locking Mechanisms and Secure Connections
You need to verify the locking mechanisms of pin connectors. Secure connections prevent accidental disconnection and maintain reliability in critical systems. You should select connectors with robust locking features, such as latches or bayonet locks. Endurance testing under specific conditions ensures that connectors remain reliable throughout their service life.
- Endurance testing validates the reliability of locking mechanisms.
- Secure connections protect against vibration and mechanical stress.
You should always prioritize locking features during the selection process. This step guarantees that your connectors deliver consistent performance and reliability.
Callout: Test & Measurement plays a vital role in evaluating the reliability of interconnects and components. You should use these tools to verify connector performance before deployment.
Cost and Availability in Pin Connector Selection
Budget Considerations
You need to balance performance and cost when you select connectors for your project. The unit cost of each connector directly affects your overall budget, especially in large-scale manufacturing. Custom connectors often require special tooling, which can increase expenses. Installation and termination costs also play a significant role. If you choose connectors that require complex installation, you may face higher labor costs. The potential cost of failure or downtime can outweigh initial savings. Reliable connectors reduce the risk of system interruptions and expensive repairs.
| Cost Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Unit cost of the connector | The price per individual connector affects overall project budget. |
| Tooling costs for custom connectors | Expenses related to creating custom connectors can significantly impact costs. |
| Installation and termination costs | Costs associated with the installation process can influence the choice of connectors. |
| Potential cost of failure or downtime | The financial implications of connector failure can lead to increased costs. |
You should always consider the total cost of ownership, not just the purchase price. A connector selection guide can help you evaluate all cost factors before making a decision.
Supplier Reliability and Lead Times
You depend on your suppliers to deliver connectors on time and at the required quality. Reliable suppliers help you avoid production delays and ensure consistent product quality. Long lead times can disrupt your schedule and increase costs. You should assess supplier track records, inventory levels, and delivery capabilities. When you work with trusted suppliers, you gain confidence in the availability of connectors for your project.
Tip: Always request lead time estimates and check supplier certifications before placing large orders.
You can reduce risk by maintaining relationships with multiple suppliers. This approach helps you secure connectors even during supply chain disruptions. You should also monitor market trends and adjust your procurement strategy as needed.
Common Mistakes in Pin Connector Selection
Overlooking Compatibility Issues
You must pay close attention to compatibility when selecting connectors. Overlooking compatibility can lead to hardware damage, system failures, or costly redesigns. You need to verify connector size, pin count, and electrical specifications. If you select the wrong connector size, you risk damaging your hardware due to incompatibility. Choosing connectors based only on appearance can result in impedance mismatches and unstable performance.
| Mistake | Impact on System Performance |
|---|---|
| Selecting the wrong connector size | Can damage hardware due to incompatibility. |
| Choosing the incorrect bandwidth | May lead to performance issues and instability. |
| Judging a connector by looks alone | Risks using unsuitable connectors affecting impedance. |
| Ignoring compression connectors | Results in poorer electrical performance and stability. |
| Using unsafe adapters | Can introduce instability and may not support power draw. |
| Ignoring manufacturer recommendations | Leads to system instability, overheating, or damage. |
You should always check datasheets and use a connector selection guide to confirm compatibility with your system requirements.
Ignoring Industry Standards
You need to follow industry standards when you select connectors. Ignoring these standards can result in non-compliant products, safety risks, and legal issues. Standards ensure that connectors meet minimum requirements for performance, safety, and interoperability. If you ignore manufacturer recommendations or use unsafe adapters, you may introduce instability or even damage your system. You should always verify that your connectors comply with relevant standards before integration.
Note: Compliance with standards protects your investment and ensures long-term reliability.
Underestimating Environmental Factors
You must consider environmental factors during connector selection. Failing to account for temperature, moisture, or vibration can shorten connector lifespan and compromise system reliability. If you underestimate these factors, you may face unexpected failures or maintenance costs. You should select connectors with appropriate ratings for your operating environment. This includes checking for moisture resistance, temperature tolerance, and mechanical durability.
You can prevent many common mistakes by following a structured connector selection guide. Careful attention to compatibility, standards, and environmental demands will help you achieve reliable and cost-effective designs.
Best Practices for Pin Connector Selection and Use
Design Tips for Pin Connectors
Layout Optimization for Connectors
You can achieve reliable performance by optimizing the layout of pin connectors on your printed circuit boards. Place connectors near the board edge for easy access, especially when working with wire-to-board types. For board-to-board connectors, align them precisely with their mating counterparts. Keep traces short and use ground planes to minimize electromagnetic interference, particularly for RF connectors. Secure mechanical stability by adding mounting holes or brackets, which is essential for connectors handling high currents. Test your design under real-world conditions to verify signal integrity, thermal performance, and mechanical durability before moving to production.
- Optimize placement for accessibility and alignment.
- Minimize signal interference with short traces and proper grounding.
- Secure connectors mechanically to prevent stress-related failures.
- Simulate and test designs to ensure robust performance.
A well-planned pinout reduces crosstalk and EMI, ensures proper power delivery, and simplifies PCB layout. Following industry standards for pinouts also improves compatibility with other systems.
Future-proofing Pin Connector Choices
You should always consider future requirements when selecting pin connectors. Choose connectors that support higher pin counts or additional features to accommodate upgrades. Adhering to industry standards ensures compatibility with new components and peripherals. Select connectors with proven reliability and availability to avoid obsolescence. This approach helps you adapt to evolving technology without major redesigns.
Installation and Maintenance of Pin Connectors
Proper Handling Techniques
Proper installation starts with clean connector cavities. Remove dirt, oil, and moisture before assembly to maintain reliable performance. Always verify that each pin is fully seated and retained after installation. Use the correct tools and follow manufacturer guidelines to avoid damaging the connectors. Document repair procedures, including connector types and pin positions, to streamline future maintenance.
- Clean all connector surfaces before installation.
- Confirm pin seating and retention.
- Use appropriate tools for assembly and disassembly.
- Keep detailed records for maintenance and repairs.
Inspection and Testing Procedures
Regular inspection and testing extend the lifespan of pin connectors. Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or misalignment during routine maintenance. Test connections with a multimeter to verify continuity and detect potential issues. Simulate operational conditions to ensure connectors perform reliably under stress. These steps help you catch problems early and maintain system integrity.
Troubleshooting Common Pin Connector Issues
Intermittent Connections and Signal Loss
You may encounter intermittent connections or signal loss in electronic assemblies. Look for symptoms such as electrical failures, loose fits, or unusual odors. Use a multimeter to check continuity and a magnifying glass to inspect for damage. Clean the connector contacts and ensure a secure fit to restore reliable operation.
Pin Damage and Wear
Pin damage and wear often result from repeated installation cycles or harsh environments. Inspect connectors visually for broken traces, bent pins, or burned components. Measure input voltage and check ground connections to rule out power supply issues. Test individual components with a multimeter to isolate faults. Regular cleaning and inspection prevent oxidation and maintain optimal electrical flow.
Tip: Consistent maintenance and careful installation practices reduce the risk of connector failures and simplify troubleshooting.
You encounter many types of connectors in modern electronics, each designed for specific tasks. The table below highlights key advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Standardization ensures versatility and cost-effectiveness | May introduce resistance and inductance in high-frequency applications |
| User-friendly design facilitates quick replacements | Durability issues with frequent insertion/removal cycles |
| Modularity allows for system expansion and upgrades | Non-shrouded headers are vulnerable to physical damage |
| Broad compatibility with various components | Potential bottleneck for thermal management |
When you select connectors, focus on voltage and current ratings, material durability, and environmental resistance. The best practice involves preparing wires cleanly, securing insertion, and testing connections. For quick reference, choose socket connectors for reliability, in-line connectors for board connections, and angle plug connectors for tight spaces. You ensure long-term performance by prioritizing reliability and compliance in every application.
FAQ
What is the difference between single-row and double-row pin connectors?
Single-row pin connectors have pins in one line. Double-row connectors arrange pins in two parallel lines. You use double-row connectors when you need more connections in a compact space.
How do you choose the right pin connector for your project?
You match the connector’s voltage, current, and pin count to your application. You check the mechanical fit and environmental ratings. You review datasheets and industry standards before making your selection.
Why do some pin connectors use gold plating?
Gold plating improves conductivity and resists corrosion. You select gold-plated connectors for high-speed data, sensitive signals, or harsh environments. Gold ensures reliable performance over many connection cycles.
Can you reuse pin connectors after disconnection?
You can reuse most pin connectors if you avoid damage during removal. You inspect pins for wear or bending before reconnecting. High-quality connectors support many mating cycles.
What standards should you check when selecting pin connectors?
You verify IEC, MIL-SPEC, UL, and RoHS compliance. These standards ensure safety, reliability, and environmental protection. You confirm certifications on datasheets or product labels.
How do you prevent signal loss in pin connector assemblies?
You use connectors with low contact resistance and proper shielding. You keep traces short and maintain secure connections. Regular inspection and cleaning help you avoid signal loss.
Are pin connectors suitable for outdoor or harsh environments?
You select connectors with moisture and corrosion resistance. You look for IP-rated housings and robust materials. These features protect your electronics in outdoor or industrial settings.
What is the typical lifespan of a pin connector?
You expect thousands of mating cycles from quality pin connectors. Lifespan depends on material, environment, and handling. You check manufacturer specifications for exact ratings.




