Electrical connectors play a vital role in every application, ensuring that power and signals transfer safely and efficiently. When you choose an electrical connector for your application, you must consider safety, reliability, and the specific environment. The rapid growth of the electrical connectors market highlights their importance:
Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
Market Size (2024) | |
Market Size (2025) | USD 91.31 billion |
Market Size (2032) | USD 147.44 billion |
CAGR (2025-2032) | 7.1% |
Region Dominance (2024) | Asia Pacific with 45.16% share |
You see applications ranging from home electronics to industrial machinery, where selecting the right M8 connector, m12 connector, or Type B connector can prevent hazards and maximize performance. The Connector factory must meet strict standards to address safety and application needs. Always focus on current, voltage, and the operating environment to ensure safety and reliability in every application.
Tip: The global connectors market is set to grow by USD 39.3 billion from 2025 to 2029, driven by electronic devices, wireless communications, and Industry 4.0.
Electrical Connectors: Definition and Importance
What Is an Electrical Connector?
You encounter electrical connectors in almost every electronic device you use. Industry standards define an electrical connector as an electromechanical device that creates a secure electrical connection between two or more parts or circuits. This connection allows you to join components into a larger system. Most connectors have two main parts: the male (plug) and the female (socket). The materials used in these connectors, such as copper alloys for conductors and specialized plastics for insulators, ensure both conductivity and safety. You will find connectors that are removable, require tools for assembly, or form permanent joints. Organizations like UL, CSA, EN/IEC, and CCC set safety standards for connectors, focusing on fire prevention, electric shock protection, and regional compliance. Communication standards, including USB and RS-232C, also specify connector types and arrangements to guarantee interoperability and reliability.
Key components of electrical connectors:
Male (plug) and female (socket) parts
Conductive materials for efficient current flow
Insulating housings for safety
Mechanical features like pin arrangements, keying, and locking mechanisms
Why Electrical Connectors Are Essential
You rely on electrical connectors to ensure the safe and efficient transfer of power and signals. These connectors protect you from hazards such as electric shock and fire by meeting strict safety certifications. In North America, UL and CSA standards focus on fire prevention, while Europe emphasizes electric shock prevention through EN/IEC standards. China enforces safety with CCC certification. These standards ensure that connectors meet minimum safety requirements, protecting users and equipment. Connectors also play a critical role in system reliability. When connectors fail, they can cause short circuits, open connections, or increased resistance, leading to system malfunctions or even dangerous situations.
Causes | Impact on System Reliability | |
|---|---|---|
Short Circuit | Moisture, corrosion | Blown fuses, signal faults, fires, critical safety issues |
Open Connection | Loose/oxidized terminals | Loss of power or signal, system malfunction |
Increased Resistance | Wear, corrosion | Faulty readings, signal loss, heat generation, potential fires |
Fretting Corrosion | Vibration, thermal cycling | Open circuits, voltage drops, power failure, signal loss |
Mechanical Wear | Misalignment, excessive force | Incomplete connections, terminal damage, safety issues |
Environmental Contamination | Dust, chemicals, dirt | Poor conductivity, corrosion, unreliable connections |
Tip: Applying connector grease can reduce friction, repel moisture, and prevent corrosion, which helps maintain reliable connections.
Core Functions of Electrical Connectors
You depend on electrical connectors to perform several vital functions in modern electronic systems. These connectors enable electrical contact between circuits or devices, allowing power and data to flow seamlessly. They ensure signal integrity and prevent interference, which is crucial for both power and data transmission. Connectors provide electrical insulation to prevent short circuits and offer mechanical support to reduce stress on wires or printed circuit boards. You benefit from easy assembly and maintenance because connectors allow quick disconnection and reconnection. This modularity makes it simple to modify or expand systems. Many connectors include keying and locking mechanisms to prevent mismating or accidental disconnection, enhancing reliability.
Main functions of electrical connectors:
Enable electrical contact between circuits
Transfer power and data
Maintain signal integrity
Provide insulation and mechanical support
Simplify assembly, maintenance, and system upgrades
Prevent mismating and accidental disconnection
You will find that connectors are essential in every application, from lighting systems to industrial machinery. They ensure stable current transfer, prevent accidental disconnections, and protect against overheating and electrical fires.
Electrical Connector Types: Comprehensive Overview

You encounter a wide range of electrical connectors in modern systems. Industry standards classify these connectors by their function, shape, and performance. The main electrical connector types include wire-to-wire, wire-to-board, and board-to-board connectors. Each type serves a unique purpose and fits specific installation needs. You also find that features like coding systems, termination methods, and housing materials help you select the right connector type for your application. For example, stainless steel housings provide durability for heavy-duty use, while plastic housings keep devices lightweight. Certifications such as UL ratings and IEC standards ensure that connectors meet safety and regulatory requirements.
Wire-to-Wire Electrical Connectors
Wire-to-wire connectors join two or more wires, allowing you to extend circuits or repair wiring. You use these connectors in both residential and industrial settings. In homes, you often see twist-on wire connectors inside junction boxes and outlets. In industrial environments, terminal blocks and quick-connect connectors enable fast assembly and flexible wiring.
Butt Connectors
Butt connectors let you join two wires end-to-end. You insert stripped wires into each end of the connector and crimp them for a secure connection. You often use butt connectors in automotive repairs and appliance wiring. They provide a reliable, insulated joint that resists vibration and moisture.
Splice Connectors
Splice connectors help you join multiple wires together. You use them when you need to split a circuit or create a branch. Splice connectors come in various forms, including tap and inline splices. You find them in control panels, lighting systems, and industrial machinery.
Twist-On Wire Connectors
Twist-on wire connectors, also known as wire nuts, are common in residential wiring. You twist the connector onto stripped wires, creating a secure and insulated connection. These connectors are easy to install and remove, making them ideal for home DIY projects and quick repairs.
Tip: Always choose the correct size of twist-on connector to match the wire gauge for a safe and reliable connection.
Wire-to-Board Electrical Connectors
Wire-to-board connectors link individual wires to printed circuit boards (PCBs). You rely on these connectors for secure, compact, and reliable connections in electronics and automation systems. They offer locking protection and friction locks, which prevent accidental disconnection. Polarized designs help you avoid mismating during assembly. Compact pitch sizes save space, making these connectors suitable for high-density connector applications.
Terminal Blocks
Terminal blocks provide a simple way to connect wires to a PCB. You secure wires using screw clamps or spring mechanisms. Terminal blocks are common in industrial control panels and distribution boards, where you need flexible wiring and easy maintenance.
IDC (Insulation Displacement Connectors)
IDC connectors let you connect wires to a PCB without stripping insulation. You press the wire into the connector, and sharp contacts pierce the insulation to make an electrical connection. IDC connectors support fast, automated assembly and are widely used in consumer electronics and household appliances.
Crimp Connectors
Crimp connectors use a metal sleeve that you compress around a wire. This method creates a strong, vibration-resistant connection. Crimp connectors are popular in automotive lighting, industrial automation, and panel-mounted connectors for printed boards.
Advantages of wire-to-board connectors:
Secure locking and retention
Space-saving design
Support for automated production
Board-to-Board Electrical Connectors
Board-to-board connectors join two or more PCBs within a device. You see these connectors in consumer electronics, medical devices, and communication equipment. They support high-speed data transfer and enable compact device designs.
Pin Headers
Pin headers consist of rows of metal pins that connect one PCB to another. You use them for stacking or parallel board arrangements. Pin headers are versatile and support various configurations.
Sockets
Sockets mate with pin headers or other connectors, providing a removable connection between boards. You use sockets in applications where you need to replace or upgrade components easily.
Edge Connectors
Edge connectors attach directly to the edge of a PCB. You find them in computer motherboards, expansion cards, and other high-density connector applications. Edge connectors support reliable, high-speed connections in compact spaces.
Board-to-board connectors enable you to design flexible, modular systems. They help you minimize space while maintaining reliable signal transmission.
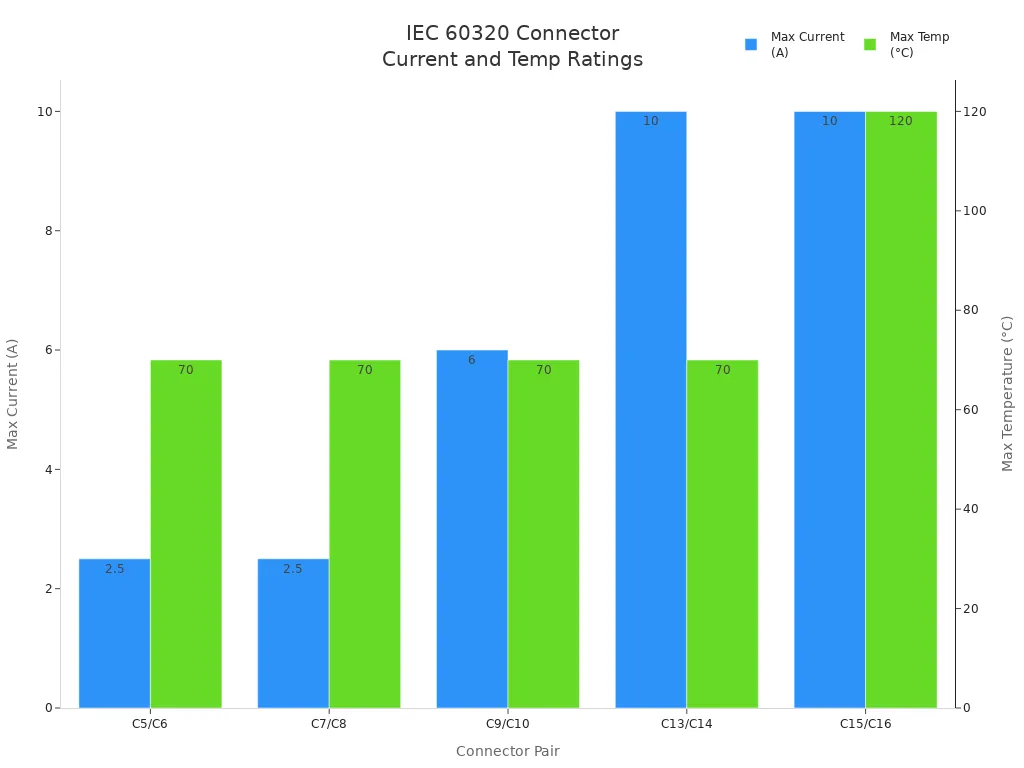
Note: Industry standards such as ANSI/IEC, IP ratings, and MIL-SPEC ensure that connectors meet performance, safety, and environmental requirements. The IEC 60320 standard, for example, classifies connector pairs by current, voltage, and temperature ratings, supporting global compatibility.
Circular Electrical Connectors
Circular electrical connectors stand out for their cylindrical design and robust performance. You often choose these connectors for applications that demand durability and environmental resistance. Their shape allows you to distribute mechanical stress evenly, which helps in harsh environments. You find circular electrical connectors in aerospace, military, and industrial automation systems.
Industrial Circular Connectors
You rely on industrial circular connectors when you need reliable connections in factories, robotics, and heavy machinery. These connectors use threaded or bayonet coupling, making them easy to connect and disconnect. The sealing with O-rings or gaskets protects against moisture, dust, and chemicals. You benefit from their high resistance to vibration and shock, which ensures stable operation in demanding settings.
Military-Grade Circular Connectors
Military-grade circular connectors meet strict standards for durability and performance. You use them in defense, aerospace, and mission-critical equipment. These connectors offer advanced sealing, corrosion resistance, and rugged shells. You can trust them to maintain connections under extreme temperatures, vibration, and mechanical stress.
Tip: Circular electrical connectors simplify maintenance because you can quickly mate or unmate them, even in tight spaces.
Rectangular Electrical Connectors
Rectangular electrical connectors provide a different set of advantages. You see these connectors in automotive electronics, networking, and consumer devices. Their box-like shape allows you to pack more pins into a smaller area, which increases signal density and supports multi-channel data.
D-Sub Connectors
D-Sub connectors have a D-shaped shell and rows of pins. You use them for computer ports, industrial controls, and instrumentation. The design helps prevent mismating and provides secure latching. You can find D-Sub connectors in both signal and power applications.
Ribbon Cable Connectors
Ribbon cable connectors connect flat ribbon cables to circuit boards or other devices. You use them in computers, printers, and communication equipment. These connectors support high pin counts and allow you to make multiple connections at once, which saves time during assembly.
Note: Rectangular connectors often require screws, latches, or clips for secure attachment. This design can take more effort to install but offers strong retention.
Circular vs. Rectangular Connectors: Key Differences
Feature | Circular Connectors | Rectangular Connectors |
|---|---|---|
Pin Configuration & Density | Pins in circles; fewer pins; lower signal density | Pins in grid; higher pin density; ideal for multi-channel and high-speed data |
Environmental Protection | Better sealed; resistant to moisture, dust, chemicals; often IP/MIL-spec rated | Sealing possible but more challenging; may need extra engineering for harsh environments |
Durability & Mechanical Strength | Cylindrical design spreads stress; rugged coupling; high vibration and shock resistance | Flat form with stress points at corners; less rugged; may need reinforcement for vibration resistance |
Ease of Mating/Unmating | Quick connect/disconnect; twist or push; good for frequent maintenance | Secured by latches, screws, or guides; more space and effort needed for connection/disconnection |
Customization & Modularity | Limited after shell and pin count chosen; variations in shell size, contact, locking | More modular with interchangeable inserts, mounting, and stackable modules; greater flexibility |
Typical Applications | Aerospace, military, industrial automation; harsh environments | Automotive, networking, consumer devices; high pin density and space efficiency |
You should consider these differences when selecting electrical connector types for your project.
Coaxial Electrical Connectors
Coaxial electrical connectors serve a unique role in high-frequency signal transmission. You use these connectors to maintain the coaxial geometry and impedance of the cable, which is critical for minimizing signal loss and reflection. This design ensures efficient transmission of radio frequency (RF) and microwave signals.
BNC Connectors
BNC connectors use a bayonet coupling mechanism. You often find them in test equipment, broadcast, and networking. Their quick connect and disconnect feature makes them ideal for laboratory and field use.
SMA Connectors
SMA connectors use a threaded coupling and support higher frequencies. You use them in wireless communication, antennas, and microwave systems. Their compact size and precise impedance matching make them suitable for demanding RF applications.
Coaxial connectors have an inner and outer conductor to preserve signal integrity.
You can choose from cable-mount, PCB-mount, or panel-mount options.
Materials like stainless steel and brass, with gold or silver plating, improve conductivity and resist corrosion.
Callout: When you select coaxial connectors, always check frequency range, power handling, and environmental resistance to match your application needs.
Power Electrical Connectors
Power connectors deliver electrical energy safely and efficiently in every system. You rely on these connectors to handle high currents and voltages, whether you work with industrial machinery or consumer devices. Selecting the right power connectors ensures safety, reliability, and compliance with industry standards.
AC Power Connectors
AC power connectors supply alternating current to equipment. You see these connectors in household outlets, industrial machines, and commercial appliances. They come in various shapes and sizes, often following regional standards for voltage and current. Many AC power connectors use color coding to help you identify phases and ground connections. In industrial settings, you often encounter rectangular HDC connectors and M-style circular connectors, which are sized by screw center distances or metric threads.
Standard | Scope and Application | Key Features and Notes |
|---|---|---|
SAE J2030 | Heavy-duty connectors for DC power systems ≤ 50 Vdc, e.g., off-highway machinery | Electrical, mechanical, and environmental tests, including contact resistance, durability, and thermal cycles |
UL 2237 | Industrial connector standard with enhanced power transmission safety requirements | No current limit, voltage limit 1 kV AC/DC, short circuit current rating ≥ 5 kA, stricter than UL 2238 |
UL 2238 | Industrial connector standard focusing on safety and performance | Includes current and voltage limits, less stringent short circuit rating than UL 2237 |
Connector Sizes | Rectangular HDC, M-style circular (M5, M8, M12) | M-style connectors have subcategories for different power and data applications |
Color Coding | Regional standards for color coding of power connectors | Supports single and three-phase power, rated up to 600 A and higher, varies by region |
Note: Always check the connector’s certification and rating before installation to ensure safe operation.
DC Power Connectors
DC power connectors provide direct current to devices such as laptops, LED lighting, and battery-powered equipment. You often use barrel connectors, snap-in types, or specialized locking connectors for secure and stable connections. In automotive and industrial environments, you see connectors designed for vibration resistance and high current loads. These connectors must meet standards for contact resistance, durability, and thermal cycling to guarantee long-term performance.
Data and Signal Electrical Connectors
Data and signal connectors transmit information and control signals between devices. You depend on these connectors for high-speed data transmission and reliable communication in computers, networks, and multimedia systems.
USB Connectors
USB connectors have become the universal standard for connecting peripherals, charging devices, and transferring data. You use USB Type-A, Type-B, and USB-C connectors in computers, smartphones, and industrial equipment. These connectors support high bandwidth capabilities and power delivery, making them essential for modern electronics.
HDMI Connectors
HDMI connectors transmit high-definition video and audio signals between devices. You find these connectors in TVs, monitors, gaming consoles, and projectors. HDMI connectors support high-speed data transfer and high bandwidth capabilities, which are critical for clear, uncompressed digital signals.
RJ45 (Ethernet) Connectors
RJ45 connectors enable wired network connections in homes, offices, and data centers. You use these connectors for Ethernet cables, which support high-speed data transmission and reliable signal integrity. RJ45 connectors feature precise pin layouts and locking tabs to prevent accidental disconnection.
At high frequencies, transmission line effects increase signal loss, requiring careful connector design.
Impedance matching and optimized pin layouts reduce reflection and crosstalk, preserving signal clarity.
Testing with advanced equipment ensures connectors meet the demands of modern high-speed protocols.
Tip: Always select connectors rated for your required data rate to maintain signal integrity in demanding applications.
Specialty Electrical Connectors
Specialty electrical connectors address unique challenges in harsh or demanding environments. You need these connectors for automotive, marine, and industrial applications where standard connectors may fail.
Automotive Connectors
Automotive electrical connectors must withstand vibration, temperature changes, and exposure to chemicals. You find these connectors in engine control units, lighting systems, and CAN networks. Secure locking mechanisms, watertight seals, and rugged shells ensure reliable performance in vehicles.
Waterproof Connectors
Waterproof connectors protect sensitive circuits from moisture, dust, and contaminants. You use these connectors in outdoor lighting, marine equipment, and industrial automation. High ingress protection ratings (IP67, IP68, IP69K) and robust sealing materials like rubber and silicone provide long-term durability.
High-Temperature Connectors
High-temperature connectors operate in environments with extreme heat, such as industrial engines or aerospace systems. You rely on materials like titanium, ceramics, and high-performance polymers to resist temperatures up to 405°C or higher. These connectors maintain signal integrity and mechanical strength under continuous thermal stress.
Specialty connectors use corrosion-resistant metals, high-performance plastics, and advanced sealing to ensure durability.
Reliable locking mechanisms and precise contact alignment prevent accidental disconnection and maintain stable connections.
Callout: Always verify that specialty connectors meet the required standards for your application, including resistance to vibration, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
Applications of Electrical Connectors Across Industries

Electrical Connectors in Consumer Electronics
You interact with electrical connectors every day through your phones, laptops, and entertainment devices. These connectors enable reliable power delivery and seamless data transfer in compact, user-friendly designs. The most prevalent types in consumer electronics include:
Barrel (coaxial) connectors: You find these in devices like routers and portable speakers. Their cylindrical shape supports DC voltages from 5V to 24V and offers a simple, robust connection.
IEC connectors: These power your desktop computers and monitors. Their standardized design, recessed pins, and grounding features ensure safety and global compatibility.
USB connectors: USB-C stands out for its reversible design and ability to deliver up to 100W of power. You use USB connectors for charging, data transfer, and even video output.
Lightning connectors: If you use Apple devices, you benefit from the reversible and robust Lightning connector, though USB-C is replacing it in newer models.
SATA power connectors: These supply power to storage devices inside computers, supporting multiple voltages in a single, compact connector.
You rely on these connectors because they balance safety, compactness, and versatility. Their design supports the demanding applications of modern consumer electronics, from charging to high-speed data transfer.
Electrical Connectors for Industrial Equipment
In industrial environments, you need electrical connectors that withstand harsh conditions and deliver reliable performance. The requirements for these connectors differ significantly from those in consumer electronics. The following table highlights key differences:
Connector Type | Typical Application | Current Handling Capacity | Physical Design & Features | Safety & Environmental Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IEC C7/C8 (“Figure-8”) | Consumer electronics (e.g., gaming consoles, radios) | Low (up to 10A) | Compact, non-polarized or polarized | Designed for low power, minimal ruggedness |
DC Barrel Connectors | Small consumer electronics | Low | Cylindrical, various diameters | Low voltage, compact size |
Anderson Powerpole Connectors | Industrial equipment, backup power systems | High | Modular, supports high current | Rugged, designed for harsh environments |
M12 X-Coded Connectors | Industrial Ethernet | Moderate to high | Ruggedized, secure locking mechanism | Resistant to dust, moisture, vibration |
IEC C13/C14 and C19/C20 | Enterprise IT, data centers | Medium to high (10A-20A) | Standardized, robust for server power | Meets safety standards for higher voltage loads |
You select connectors for industrial applications based on their ability to handle higher currents, resist dust and moisture, and survive vibration. Features like secure locking mechanisms and ruggedized housings ensure that your equipment operates safely and reliably, even in challenging environments.
Tip: Always verify that your connectors meet the required safety and environmental standards for your specific industrial application.
Automotive and Transportation Connectors
When you work with automotive and transportation systems, you face unique challenges. Automotive electrical connectors must deliver high-speed connectivity while remaining lightweight and easy to install. You need connectors that can withstand vibration, shock, extreme temperatures, and exposure to chemicals. Compact size is essential because space is limited in vehicles.
Key challenges and requirements include:
High reliability and durability for safety-critical systems
Resistance to vibration, shock, and electromagnetic interference
Operation across wide temperature ranges, from -55°C to 125°C
Sealing against moisture and chemicals, meeting IP65, IP67, and IP69 standards
Support for high amperage charging and fast data transmission in electric vehicles
Prevention of misalignment and bent pins during assembly
Innovations such as plug-only landed contact designs and floating board-to-board connectors help you address assembly and reliability issues. Ruggedized materials and advanced power contact technologies allow you to meet the demands of modern vehicles while reducing cost and installation complexity.
You depend on automotive electrical connectors to ensure safe, efficient, and reliable operation in every transportation application, from traditional cars to electric and hybrid vehicles.
Aerospace and Defense Electrical Connectors
You face some of the most demanding environments when working with aerospace and defense applications. Here, electrical connectors must deliver absolute reliability under extreme conditions. You often encounter connectors that must withstand vibration, shock, moisture, and electromagnetic interference. These requirements ensure that systems in aircraft, missiles, satellites, and ground vehicles perform flawlessly.
Military and aerospace standards, known as MIL-DTL specifications, set strict guidelines for these connectors. These standards define the mechanical, electrical, and environmental characteristics needed for mission-critical performance. The table below highlights some of the most important standards and their typical applications:
Standard | Description | Key Features and Applications |
|---|---|---|
MIL-DTL-83513 | Micro-D connectors | Polarized shell, micro-miniature, robust, low contact resistance, high current, used in missiles, avionics, satellites |
MIL-DTL-38999 | High-density circular connectors | Quick-disconnect, EMI shielding, vibration and corrosion resistant, used in avionics, missiles |
MIL-DTL-26482 | Compact circular connectors | Smaller size, bayonet/threaded coupling, environmentally sealed, used in ground vehicles, portable equipment |
MIL-DTL-24308 | Miniature D-sub connectors | Polarized shell, rack and panel, designed for space/weight critical applications like aircraft and missiles |
You rely on these connectors because they offer high mechanical durability, EMI/RFI shielding, and environmental sealing. The shell geometry, contact plating, and standardized pin layouts guarantee interoperability and backward compatibility. When you select electrical connectors for aerospace and defense, you ensure that every connection can endure thermal extremes, mechanical stress, and environmental exposure. These features protect both system performance and lives.
Tip: Always verify that your connectors meet the relevant MIL-DTL standard for your specific aerospace or defense application.
Medical Device Connectors
In medical device applications, you must prioritize safety, reliability, and hygiene. Electrical connectors in this field support life-saving equipment, such as patient monitors, imaging systems, and surgical tools. You need connectors that provide secure, error-free connections and withstand repeated sterilization cycles.
You often choose connectors with color coding, keying, and locking mechanisms to prevent accidental disconnection or misconnection. Many medical connectors use materials that resist chemicals and support easy cleaning. You also benefit from compact designs that fit into handheld or wearable devices.
Key requirements for medical device connectors include:
Biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization chemicals
Secure locking to prevent accidental disconnects
High mating cycle durability for frequent use
Shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference with sensitive equipment
You select electrical connectors that comply with medical standards and certifications, ensuring patient safety and device reliability. These connectors play a vital role in applications where failure is not an option.
Note: Always check for compliance with medical device regulations and standards before selecting connectors for healthcare applications.
Telecommunications Connectors
Telecommunications applications demand connectors that support high-bandwidth and low-latency communication. You use these connectors in data centers, fiber optic networks, and 5G infrastructure. The right choice ensures stable, high-speed data transmission over long distances.
Fiber optic connectors, such as LC/APC, provide ultra-low back reflection and low insertion loss. This design minimizes signal interference and maintains high signal quality, which is essential for telecom networks and data centers. You benefit from their compact, high-density form, which fits space-constrained environments and supports bandwidth-intensive applications.
RF connectors for 5G systems operate at very high frequencies, including millimeter-wave bands. These connectors maintain precise impedance matching and low signal loss, preserving signal integrity at high data rates. Their mechanical precision prevents misalignment, and their environmental durability ensures reliable operation in various conditions.
Choose connectors that match your required data rate and environmental conditions.
Look for features like EMI shielding, secure locking, and compatibility with singlemode fiber for long-distance transmission.
Callout: Reliable telecommunications connectors enable you to deliver ultra-fast data speeds and low latency, supporting advanced applications like enhanced mobile broadband and massive IoT.
Renewable Energy System Connectors
You play a crucial role in the success of renewable energy systems when you select the right connectors. In solar, wind, and battery storage applications, you need electrical connectors that can handle high currents, resist harsh weather, and maintain reliable performance over time. These connectors must support both DC and AC circuits, often in outdoor environments where temperature and humidity fluctuate.
You often encounter MC4 connectors in solar photovoltaic installations. These connectors allow you to connect solar panels quickly and securely. Their locking mechanism prevents accidental disconnection, and their weatherproof design protects against dust and water. In wind energy systems, you use heavy-duty circular connectors to link turbines, control units, and power converters. These connectors must withstand vibration, UV exposure, and even lightning strikes.
Key features you should look for in renewable energy connectors include:
High current and voltage ratings for efficient power transfer
UV-resistant and flame-retardant materials for outdoor durability
IP67 or higher ingress protection to guard against water and dust
Secure locking mechanisms to prevent accidental disconnects
Connector Type | Typical Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
MC4 | Solar panel connections | Fast, weatherproof assembly |
Heavy-duty Circular | Wind turbines | Vibration and UV resistance |
Power Distribution | Battery storage | High current handling |
Tip: Always verify that your connectors meet local and international standards for renewable energy applications. This ensures safety and long-term reliability.
You must also consider ease of installation. Many renewable energy projects require field assembly, so you benefit from connectors with tool-free or quick-lock designs. When you choose the right electrical connectors, you help maximize system uptime and energy output.
Home and Building Automation Connectors
You rely on specialized connectors to create smart, efficient, and safe home or building automation systems. These connectors link sensors, controllers, lighting, HVAC, and security devices. In these applications, you need electrical connectors that support both power and data transmission, often in compact spaces.
You often use modular connectors like RJ45 for Ethernet-based automation networks. These connectors enable fast communication between devices and support protocols such as KNX, BACnet, and Modbus. For lighting control, you might select push-in wire connectors or terminal blocks, which simplify wiring and reduce installation time.
Important considerations for home and building automation connectors include:
Compact size for easy integration into wall boxes and panels
Color coding and keying to prevent wiring errors
Support for both low-voltage power and high-speed data
Flame-retardant and tamper-resistant housings for safety
You also benefit from connectors with tool-free installation, which speeds up deployment and maintenance. In smart homes, wireless device integration is common, but you still need reliable connectors for power and backup communication lines.
Note: Always select connectors rated for the voltage and current of your automation devices. This helps prevent overheating and ensures long-term safety.
When you choose the right electrical connectors for automation, you create systems that are easier to expand, troubleshoot, and upgrade. This flexibility supports the evolving needs of modern buildings and smart homes.
How to Select the Right Electrical Connector
Choosing the right electrical connector for your application requires careful analysis of electrical, mechanical, and environmental factors. You must match connector specifications to your system’s needs to ensure safety, signal integrity, and reliable connections. This section guides you through the essential criteria for connector selection, helping you avoid common pitfalls and optimize performance.
Electrical Requirements for Connectors
Voltage and Current Ratings
You must always start your connector selection by evaluating voltage and current ratings. These ratings define the maximum electrical pressure and current a connector can safely handle. If you exceed these limits, you risk insulation failure, arcing, overheating, and even fire hazards. Connectors with voltage ratings below your system’s requirements can lead to code violations and unsafe conditions. Using connectors with higher voltage ratings than your circuit voltage adds a safety margin.
Voltage ratings depend on insulation material and the spacing between contacts. The rated voltage is the maximum recommended working voltage.
Current ratings control the temperature rise inside connectors. Exceeding the rated current causes heat buildup, damaging insulation and contacts.
Multicore connectors require derating of current per contact to prevent overheating.
Always check for clear voltage and current markings and certifications to ensure compliance with safety standards like UL and NEC.
Tip: Select connectors that meet or exceed your system’s voltage and current requirements for safe and reliable operation.
Key electrical parameters also include contact resistance, insulation resistance, and dielectric strength. Low contact resistance ensures minimal heat generation, especially in high-current applications. Strong insulation and high dielectric strength are critical for high-voltage environments.
Signal Type: Power vs. Data
You must distinguish between connectors designed for power and those for data. Power connectors focus on handling high currents and voltages, while data connectors prioritize signal integrity and low signal loss. For high-frequency or high-speed data applications, you need connectors with precise geometry and materials that support low return loss and optimal voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR). These factors help maintain signal integrity and prevent data errors.
Power connectors require robust contacts and insulation to manage steady-state and surge currents.
Data connectors must minimize interference and preserve low signal loss, especially in applications like Ethernet or HDMI.
For mixed-signal applications, select connector types that separate power and data paths to avoid crosstalk.
Note: Always match the connector’s electrical characteristics to your application’s signal type to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Mechanical Considerations for Electrical Connectors
Size and Form Factor
You need to consider the physical size and form factor of connectors to ensure compatibility with your device or system. Space constraints often dictate the choice of connector type, especially in compact electronics or densely packed control panels. The connector must accommodate the required lead diameters and support low-profile or flush-mount designs for board stacking.
Mechanical Factor | Description | Supporting Details |
|---|---|---|
Size | Must fit available space and support required lead diameters | Lead acceptance ranges from 0.008–0.065” diameter; minimal length for compact assemblies |
Precision | Essential for small devices and complex systems | Precision machining enables tight dimensional control and complex features |
You benefit from connectors available in various mounting options, such as solder-mount or press-fit, to suit different assembly processes.
Mating Cycles and Durability
Durability is crucial, especially in industrial or high-use environments. You should select connectors rated for the number of mating cycles your application demands. High-quality materials like beryllium copper or beryllium nickel provide superior resistance to temperature extremes, shock, vibration, and moisture. Gold plating on contacts ensures low contact resistance and long-term reliability.
Frequent insertions and extractions require connectors with robust mechanical design.
Precision-machined receptacles and tailored internal contacts improve durability and maintain reliable connections over time.
Callout: Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for mating cycle ratings to match your application’s maintenance and usage patterns.
Locking Mechanisms
Locking mechanisms play a vital role in maintaining secure connections, especially in environments subject to vibration or movement. You can choose from threaded, bayonet, latch, or snap-in designs. These features prevent accidental disconnection and ensure consistent electrical contact.
Industrial and automotive applications often require connectors with strong locking features.
Locking mechanisms also help maintain signal integrity by preventing micro-movements that could disrupt the connection.
Tip: Select connectors with locking mechanisms suited to your application’s mechanical stresses and maintenance needs.
Environmental Factors in Connector Selection
Temperature Range
You must evaluate the temperature range your connectors will face. High temperatures cause thermal stress, degrading materials and reducing connector lifespan. For applications exposed to extreme heat or cold, select connectors made from materials rated for those conditions.
Materials like beryllium copper and high-performance polymers resist temperature extremes.
Connectors for outdoor or industrial use often specify operating temperature ranges to ensure reliability.
Moisture and Waterproofing
Moisture poses a significant threat to connector reliability. Water ingress can cause corrosion, short circuits, and insulation failure. For outdoor, marine, or industrial applications, choose connectors with high ingress protection (IP) ratings. Specialized coatings or hermetic sealing protect against corrosive compounds like acids or salt spray.
Dust and dirt can also interfere with connections, so select connectors with appropriate sealing for your environment.
UV-resistant materials are necessary for outdoor use to prevent brittleness and material degradation.
Vibration and Shock Resistance
Vibration and shock can loosen connections and cause intermittent faults. You should select connectors with mechanical features designed to resist these forces. Locking mechanisms, rugged housings, and precision contacts all contribute to maintaining reliable connections in harsh environments.
Industrial, automotive, and aerospace applications demand connectors tested for vibration and shock resistance.
Environmental conditions often worsen mechanical stresses, so robust design is essential for long-term reliability.
Note: Environmental factors like temperature, moisture, and vibration directly impact connector durability and performance. Always match connector specifications to your application’s environmental challenges.
Application-Specific Needs for Electrical Connectors
When you select electrical connectors, you must address needs that go beyond basic electrical and mechanical requirements. Each application brings unique challenges, so you must consider compliance, ease of installation, and cost factors to ensure a successful selection.
Compliance and Standards
You cannot overlook compliance and standards when choosing connectors for regulated industries. Certified connectors provide more than just basic functionality. They deliver greater electrical, mechanical, and functional safety. You benefit from improved fire protection and enhanced flame-retardant properties, which are essential in mission-critical environments.
Certified connectors offer special protections tailored to your specific application scenario.
Using certified components maximizes uptime and reduces interference, especially in industries like transportation, energy, manufacturing, and medical devices.
Compliance with standards such as UL 2238, UL 60950-1, CE marking, and DNV GL certification ensures your connectors meet global and regional regulations.
Certification involves a rigorous process, including real-life testing, evaluation, and ongoing re-certification, so you can trust the reliability and safety of your selection.
Industry standard compliance promotes market standardization, reduces total cost of ownership, and drives innovation by meeting evolving regulatory requirements.
Tip: Always verify that your connector selection aligns with the latest industry standards to ensure safety, reliability, and market access for your application.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
You should prioritize connectors that simplify installation and maintenance. Easy-to-install connectors reduce labor time and minimize the risk of wiring errors. Features such as tool-free assembly, color coding, and clear labeling help you achieve faster and more accurate installation.
Quick-locking mechanisms and modular designs allow you to replace or upgrade connectors without disrupting the entire system.
Connectors with high mating cycle ratings support frequent maintenance, which is crucial in applications that require regular inspection or replacement.
Clear documentation and compatibility with standard tools further streamline the installation process.
When you choose connectors designed for easy maintenance, you improve system uptime and reduce long-term operational costs.
Cost and Availability
Cost and availability play a significant role in your connector selection process. You must balance performance with budget constraints, especially in large-scale or cost-sensitive applications.
Standardized connectors often offer better availability and lower costs due to mass production and widespread use.
Specialty connectors may carry higher upfront costs but provide long-term savings through enhanced durability and reduced downtime.
You should also consider lead times and supply chain reliability, especially for applications with tight project schedules.
Note: Selecting connectors that are readily available and supported by multiple suppliers helps you avoid delays and ensures consistent performance throughout your application’s lifecycle.
Step-by-Step Electrical Connector Selection Process
A structured approach to connector selection ensures you address all critical factors for your application. Follow these steps to make informed decisions and achieve optimal results.
Define Application Requirements
Start by clearly defining your application’s requirements. Identify the environment, electrical loads, signal types, and any regulatory constraints. Consider the number of connections, space limitations, and expected maintenance cycles.
Determine if your application involves power, data, or mixed signals.
Assess environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, vibration, and exposure to chemicals.
List any industry-specific standards or certifications required for your application.
Shortlist Suitable Electrical Connector Types
Once you understand your application’s needs, create a shortlist of connector types that fit those requirements. Evaluate options based on:
Number of contacts needed for power and data signals
Connector gender (pin or socket) for device and cable roles
Locking type (threaded, bayonet, push-pull, snap-in) for secure connections
Shielding needs for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
Compatibility with wire size and termination method (solder, crimp, IDC, etc.)
A well-prepared shortlist streamlines your selection and narrows your focus to the most appropriate solutions.
Evaluate Against Selection Criteria
With your shortlist in hand, evaluate each connector type against detailed selection criteria:
Selection Criteria | What to Check |
|---|---|
Current and Voltage Rating | Meets or exceeds application requirements |
Environmental Resistance | Suitable IP rating, temperature, and chemical resistance |
Mechanical Fit | Size, weight, and engagement force match your application |
Durability | Mating cycles and material strength |
Compliance | Meets all required certifications and standards |
Cost and Availability | Fits budget and supply chain needs |
Callout: Use coding features and keying to prevent mismating and ensure correct alignment during installation.
Test and Validate
Before finalizing your connector selection, test and validate your choice in real-world conditions. Install connectors in a prototype or pilot system to verify performance under actual loads and environmental stresses.
Check for secure mating, signal integrity, and resistance to vibration or moisture.
Confirm that connectors meet all regulatory and safety requirements.
Gather feedback from installation and maintenance teams to identify any usability issues.
Testing and validation help you catch potential problems early, ensuring your final selection delivers reliable performance throughout your application’s lifecycle.
Practical Tips for Choosing Electrical Connectors
Matching Electrical Connector Types to Real-World Applications
Selecting the right connectors for your project requires you to match their features to your specific application. You can follow these best practices to ensure a reliable and safe connection:
Understand your electrical requirements. Check current, voltage, frequency, and signal type to ensure the connectors meet your circuit’s needs.
Consider mechanical constraints. Evaluate size, pitch, mating cycles, mounting type, and locking mechanisms to fit your design and usage frequency.
Assess environmental factors. Look at temperature range, moisture, dust, vibration, and IP ratings to guarantee durability and reliability.
Balance your budget and availability. High-performance connectors, such as RF connectors, may cost more but offer essential features.
Match connector types to applications. Use wire-to-board connectors for automotive and industrial equipment, RF connectors for high-frequency devices, circular connectors for harsh environments, and USB or RJ45 connectors for consumer electronics and networking.
Always check datasheets for pin count, voltage, current ratings, and keying to avoid mismatches.
Consider lifecycle costs and durability. Some connectors may have a higher initial cost but offer lower maintenance and longer lifespan.
Home DIY Projects
For home DIY projects, you often need connectors that are easy to use and safe. Twist-on wire connectors and push-in connectors work well for basic wiring tasks. Always match the connector size to your wire gauge and follow manufacturer instructions. Use voltage testers and wire strippers to ensure a secure and code-compliant installation.
Industrial Automation
In industrial automation, you must select connectors that resist dust, moisture, and vibration. M12 circular connectors and terminal blocks provide robust connections for sensors and actuators. Look for connectors with high IP ratings and locking mechanisms to maintain performance in harsh environments.
Automotive Repairs
Automotive repairs demand connectors that withstand vibration, temperature changes, and exposure to chemicals. Use sealed automotive connectors with secure locking features. Always check for compatibility with both solid and stranded wires, and confirm that the connectors meet the required electrical load.
High-Reliability Applications
For high-reliability applications, such as aerospace or medical devices, you need connectors that meet strict standards. Choose connectors rated for extreme temperatures, high mating cycles, and electromagnetic interference protection. Review datasheets for compliance with industry certifications and ensure proper installation to avoid failures.
Common Mistakes When Selecting Connectors
You can avoid many common mistakes by following a few simple guidelines:
Do not twist wires improperly before applying connectors. This can lead to insecure connections.
Avoid selecting the wrong connector size for your wire gauge or quantity.
Always follow manufacturer instructions for installation.
When joining solid and stranded wires, adhere to guidelines to prevent poor connections.
Strip wire insulation carefully to avoid damaging conductors.
Use the correct tools, such as wire strippers and voltage testers, for safety.
Do not over-tighten connectors, as this can damage wires or the connector itself.
Perform pull tests to verify the security of your connections.
Pay attention to wire color codes and ratings to prevent improper connections and overheating.
Tip: Careful preparation and attention to detail help you achieve safe, reliable, and code-compliant connections.
Resources for Electrical Connector Selection Help
You have access to many resources to help you choose the right connectors:
Manufacturer datasheets and catalogs provide detailed specifications, including voltage, current, pin count, and environmental ratings.
Industry standards organizations, such as UL, IEC, and MIL-SPEC, offer guidelines for connector selection and compliance.
Online selector tools from connector manufacturers can help you filter options based on your requirements.
Technical support teams and application engineers can answer your questions about compatibility and installation.
Educational videos and tutorials demonstrate proper connector use and installation techniques.
Note: Always consult multiple resources to verify your connector selection and ensure it meets your application’s needs.
You play a critical role in ensuring safety when you select the right electrical connector for your application. The correct choice protects against hazards, improves safety, and supports long-term reliability. You should always apply the selection criteria from this guide to maximize safety and performance. For complex or specialized connector needs, consult manufacturers or industry experts to guarantee the best results.
FAQ
What is the difference between a plug and a socket?
You use a plug as the male part of a connector. You use a socket as the female part. The plug inserts into the socket to create an electrical connection.
How do you know which connector type to choose?
You should check your application’s voltage, current, and environment. You also need to consider size, locking features, and compliance with standards. Always review datasheets for compatibility.
Can you reuse electrical connectors?
You can reuse some connectors, such as screw terminal blocks or certain plug-and-play types. Crimped or soldered connectors usually require replacement after removal to maintain safety and reliability.
What does IP rating mean for connectors?
IP rating shows how well a connector resists dust and water. Higher numbers mean better protection. For example, IP67 connectors resist dust and can handle temporary water immersion.
Why do some connectors have gold-plated contacts?
Gold plating resists corrosion and ensures low contact resistance. You get more reliable connections, especially in harsh or high-frequency environments.
How do you prevent connector failure?
You should select connectors rated for your environment and application. Install them correctly, avoid overloading, and perform regular inspections. Use protective covers or sealing when needed.
Are all connectors interchangeable?
No, connectors are not always interchangeable. You must match size, pin layout, voltage, and mechanical features. Always check manufacturer specifications before connecting different types.
What tools do you need for connector installation?
You may need wire strippers, crimpers, screwdrivers, or soldering irons. Some connectors offer tool-free installation. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for best results.




