Selecting the right RJ45 plug for your ethernet cable ensures reliable networking performance. Proper compatibility between RJ45 plugs and ethernet cable types prevents common issues in network connections. Many users experience link speed drops, autonegotiation failures, or no connection at all due to mismatched RJ45 plugs or incorrect wiring. Problems often result from using non-compliant cables, poorly crimped plugs, or loose connectors. You can avoid these pitfalls by following standardized wiring schemes and using professional tools. In ethernet networking, Connector factory standards help ensure quality, while specialized connectors like M8 connector and Type B connector serve unique industrial needs.
- Typical problems from poor RJ45 plug selection:
- Link operates at lower speeds
- Frequent disconnections
- Poor signal quality
RJ45 Plugs and Ethernet Cable Compatibility Basics
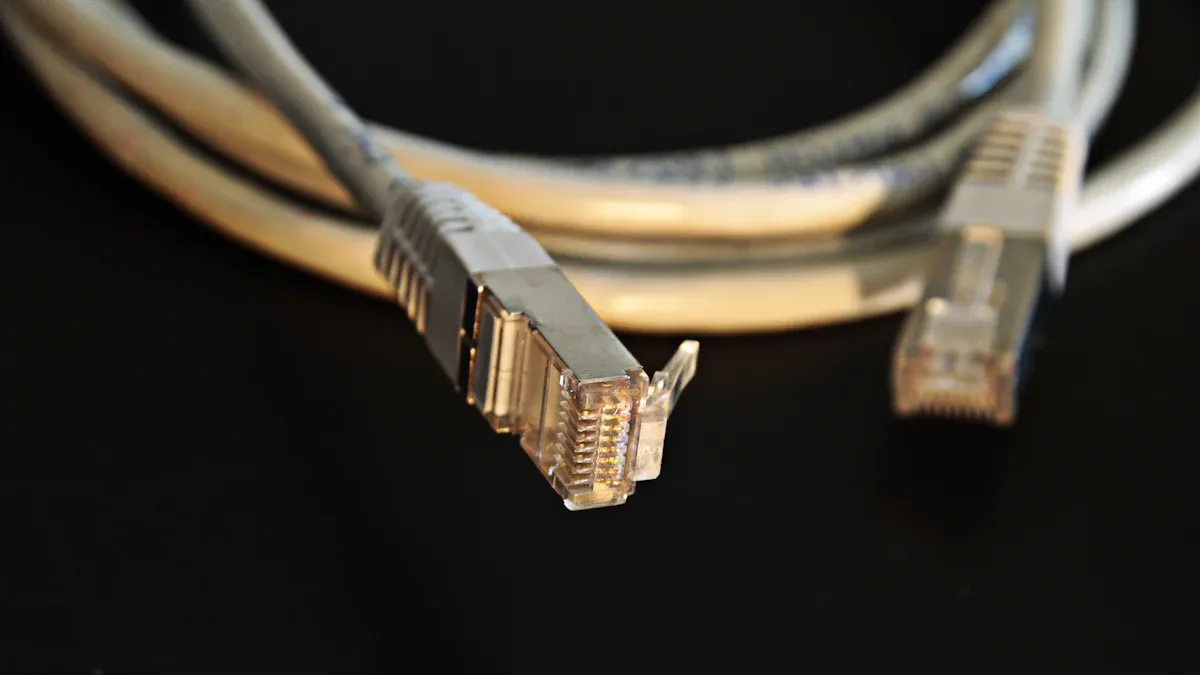

What Is an RJ45 Plug?
You encounter RJ45 plugs in almost every modern networking setup. An RJ45 plug is a modular connector with eight positions and eight contacts (8P8C). This design allows you to connect four twisted pairs of wires inside an Ethernet cable. The plug features a locking tab that secures the connection and prevents accidental disconnection. Industry standards such as ANSI/TIA-1096-A and IEEE 802.3 ensure that every RJ45 connector meets strict requirements for physical dimensions, electrical performance, and interoperability. These standards also define wiring pinouts—T568A and T568B—so you can maintain consistent signal transmission and avoid wiring errors. RJ45 connectors support both data and Power over Ethernet (PoE), making them essential for reliable networking in homes, offices, and industrial environments.
Tip: Always use RJ45 connectors that comply with FCC and international standards to guarantee compatibility and network reliability.
| Standard/Organization | Definition/Function Related to RJ45 Plug |
|---|---|
| ANSI/TIA-1096-A | Defines physical and electrical performance requirements for RJ45 connectors |
| TIA/EIA-568A & 568B | Specifies wiring pinouts for RJ45 used in Ethernet cabling |
| TIA-568-C/D | Updated structured cabling standards including Cat 5e to Cat 8 cables |
| IEEE 802.3i | Defines 10BASE-T Ethernet over twisted pair using RJ45 |
| IEEE 802.3u | Defines 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet using RJ45 |
| IEEE 802.3ab | Defines 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet over twisted pair with RJ45 |
| IEEE 802.3an | Defines 10GBASE-T 10 Gigabit Ethernet using RJ45 |
| IEEE 802.3bz | Defines 2.5G and 5G Ethernet using RJ45 |
| IEEE 802.3af | Defines Power over Ethernet (PoE) up to 15.4W over RJ45 cables |
| IEEE 802.3at | Defines PoE+ up to 25.5W over RJ45 cables |
| IEEE 802.3bt | Defines PoE++ up to 60W/100W over RJ45 cables |
| ISO/IEC 11801 | International standard for structured cabling systems using RJ45 |
| FCC Part 68 | U.S. telecom standard regulating modular connectors like RJ45 |
| IEC 60603-7 | Defines electrical performance of RJ45 connectors from Cat 5 to Cat 8 |
| EN 50173 | European structured cabling standard compatible with RJ45 systems |
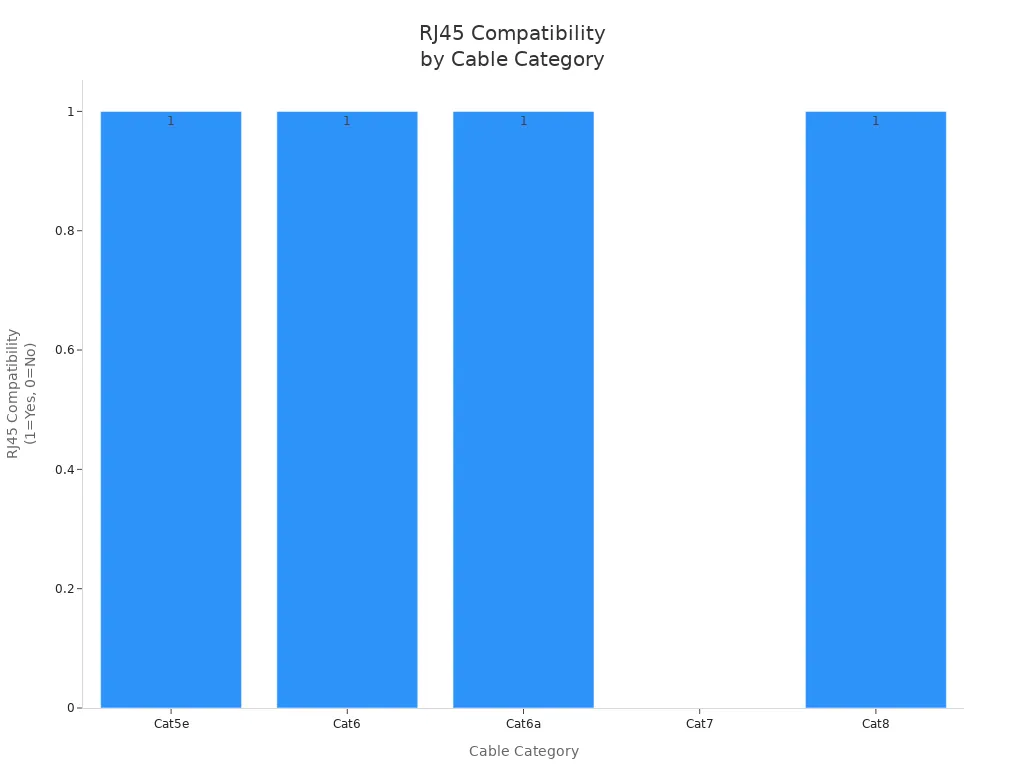
RJ45 Connector Categories and Cable Types
RJ45 connectors are not all the same. You must match the connector to the cable category for optimal performance. The following table summarizes compatibility and usage notes for each major Ethernet cable type:
| Cable Category | Connector Compatibility | Connector Type | Notes on Compatibility and Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cat5e | Compatible | RJ45 (8P8C) | Standard RJ45 connectors used; supports up to 1 Gbps; widely used in small to medium networks. |
| Cat6 | Compatible | RJ45 (8P8C) | Requires Cat6-compatible connectors and components for optimal performance; supports up to 10 Gbps over limited distance. |
| Cat6a | Compatible | RJ45 (8P8C) | Supports 10 Gbps up to 90m; thicker cable; requires matching Cat6a components. |
| Cat7 | Not Compatible | Proprietary | Does not use RJ45 connectors; uses proprietary connectors; not IEEE standardized; thicker shielding; used in specialized environments. |
| Cat8 | Compatible | RJ45 (8P8C) | Designed for high-speed data centers; supports up to 40 Gbps over short distances; requires specific components. |
Cat5e Compatibility
You can use standard RJ45 connectors with Cat5e cables. Cat5e supports up to 1 Gbps speeds and is common in home and small office networking. Always terminate Cat5e cables with 8P8C RJ45 plugs to ensure proper signal transmission.
Cat6 Compatibility
Cat6 cables require Cat6-rated RJ45 connectors for best results. These connectors handle higher frequencies and improved shielding. Cat6 supports up to 10 Gbps over short distances, but you must use the correct plug to maintain performance.
Cat6a Compatibility
Cat6a cables support 10 Gbps speeds up to 90 meters. You need Cat6a-compatible RJ45 connectors because the cable is thicker and has more shielding. Using the right plug ensures you get the full benefit of Cat6a’s performance.
Cat7 and Cat8 Compatibility
Cat7 cables use proprietary connectors, not standard RJ45 plugs. For Cat8, you can use RJ45 connectors, but only those rated for Cat8 performance. Cat8 supports up to 40 Gbps over short distances and is ideal for data centers and high-speed networking.
Key RJ45 Plug Compatibility Rules
You must follow several rules to ensure RJ45 plug and cable compatibility:
- Always use the TIA/EIA-568 wiring standard for universal compatibility.
- Choose either T568A or T568B pin configuration and use it consistently on both ends.
- Select RJ45 connectors with eight pins to match the eight wires in Ethernet cables.
- Keep wire pairs twisted as close to the connector as possible to reduce interference.
- Crimp the plug securely so metal contacts pierce the wire insulation.
- Match the connector to the cable category—Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, or Cat8.
- Do not mix wiring standards on the same cable.
- Limit untwisting of pairs to maintain signal quality.
- Test each cable after crimping to verify correct wiring.
- Use strain relief boots to protect the connector and cable.
Note: Following these rules ensures your RJ45 connectors deliver reliable performance and long-term durability in any networking environment.
Types of RJ45 Plugs and Connectors
Shielded vs. Unshielded RJ45 Connectors
You will encounter two main types of RJ45 connectors: shielded and unshielded. Shielded RJ45 connectors include a metal shell that acts as a Faraday cage, grounding the cable shield to block electromagnetic interference (EMI). This design preserves signal integrity, reduces crosstalk, and supports higher data rates, especially in environments with significant EMI. Unshielded RJ45 connectors use a plastic housing and rely on the cable’s twisted pairs to reduce noise. These connectors offer flexibility and cost savings but provide less protection against EMI.
| Feature | Shielded (STP) RJ45 Connector | Unshielded (UTP) RJ45 Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Metal shell, grounds cable shield | Plastic housing, no metal shield |
| EMI Protection | Strong EMI/RFI shielding, maintains signal integrity | Susceptible to EMI, relies on twisted pairs |
| Installation | More complex, requires grounding | Simple, no grounding needed |
| Cost | Higher, due to metal parts | Lower, widely available |
| Performance | Supports up to 10 Gbps, reduces crosstalk | Prone to EMI errors, reduced real-world performance |
| Durability | Robust, resists physical damage | Less rugged, best for short or desktop runs |
| Compatibility | Must use with shielded cables | Used with unshielded cables |
When to Use Shielded RJ45 Plugs
You should use shielded RJ45 connectors in environments with high EMI or RFI, such as industrial plants, data centers, or areas near large electrical equipment. Shielded connectors are essential for telecommunication networks with strict error tolerances and for maintaining reliable high-speed data transmission. Always pair shielded RJ45 plugs with shielded cables to ensure full EMI protection. This combination stabilizes connections and reduces errors in challenging environments.
- Recommended environments:
- Industrial and manufacturing settings with heavy machinery
- Data centers with dense cabling and high data rates
- Hotels or commercial kitchens near large electrical devices
- Telecommunication rooms with sensitive equipment
Tip: Proper grounding of shielded connectors is critical. Without grounding, the shield cannot block interference effectively.
When Unshielded RJ45 Connectors Are Sufficient
You can use unshielded RJ45 connectors in clean electrical environments where EMI is minimal. These connectors work well in homes, small offices, classrooms, and administrative areas. Unshielded connectors offer a cost-effective and simple solution for most standard networking needs.
Pass-Through vs. Standard RJ45 Plugs
RJ45 plugs come in two main designs: pass-through and standard. Each type offers unique advantages for different applications of RJ45.
Pros and Cons of Pass-Through RJ45 Connectors
Pass-through RJ45 plugs allow you to thread wires through the connector body, making it easy to verify wire order before crimping. This feature reduces wiring errors and speeds up installation, especially for beginners. However, exposed copper wires can oxidize over time, which may affect durability. You will need a special crimping tool for these connectors.
| Feature | Pass-Through RJ45 Plug | Standard RJ45 Plug |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Easier, visual wire check | Requires precise wire cutting |
| Error Reduction | Lower chance of miswiring | Higher chance of wiring errors |
| Connection Reliability | More stable, higher success rate | Reliable with proper technique |
| Durability | Less durable, exposed wires | More durable, wires protected |
| Crimping Tool Requirement | Special tool needed | Standard tool compatible |
Standard RJ45 Plug Use Cases
Standard RJ45 plugs require you to trim wires to precise lengths before insertion. This method produces a compact, durable connection ideal for permanent installations. You should use standard plugs for professional, high-density, or long-term network projects where reliability is critical.
Specialized RJ45 Connectors
Modern networking demands a variety of RJ45 connector types for specialized applications.
Waterproof RJ45 Plugs
Waterproof RJ45 plugs protect connections from moisture, dust, and UV exposure. You should use these connectors for outdoor Ethernet runs, security cameras, or any application exposed to the elements.
Toolless RJ45 Connectors
Toolless RJ45 connectors allow you to terminate cables without a crimping tool. These connectors use a snap-in mechanism, making them ideal for quick repairs or field installations where you need flexibility.
Ruggedized and Keystone RJ45 Connectors
Ruggedized RJ45 connectors withstand harsh industrial environments. They resist vibration, extreme temperatures, and physical damage. Keystone RJ45 connectors fit into patch panels or wall plates, supporting structured cabling in offices and data centers.
Note: Selecting the right types of RJ45 connectors ensures your network meets both performance and environmental requirements. Always match the connector to your specific application for best results.
Matching RJ45 Plugs to Cable Specifications
Selecting the right RJ45 plug for your cable is essential for network reliability and performance. You must consider several factors beyond just the cable category label. The physical characteristics of your cable, such as jacket diameter, conductor type, and wire gauge, play a critical role in ensuring a secure and effective connection.
Matching RJ45 Connector by Cable Category
You might think that matching an RJ45 connector to your cable is as simple as reading the category label. However, the process requires more attention to detail. The fitment between the RJ45 connector and the cable depends on several physical parameters.
- Check the cable jacket outside diameter (OD) and conductor insulation diameter. RJ45 connectors are designed to fit specific ranges.
- Identify the conductor type. Solid and stranded cables require different RJ45 connector designs.
- Use shielded RJ45 connectors with shielded cables to maintain proper grounding and EMI protection. Unshielded cables pair best with unshielded connectors.
- Avoid using shielded connectors on unshielded cables, as this can cause improper fitment and reduce performance.
- For Cat6 and Cat6a cables, select RJ45 connectors with features like staggered load bars or field termination plugs. These help reduce crosstalk and support reliable 10G Ethernet performance.
- Do not rely solely on category markings on packaging. Always review the manufacturer’s technical specifications for the RJ45 connector to ensure a proper match.
- Factory pre-terminated patch cords offer the highest quality for solid copper cables. If you must terminate cables yourself, use strain relief boots and test each connector before installation.
Tip: Reputable manufacturers provide detailed specifications for their RJ45 connectors. Always consult these documents to verify compatibility with your cable.
| Cable Category | Recommended RJ45 Connector Features | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Cat5e | Standard 8P8C, unshielded or shielded as needed | Match OD and conductor type |
| Cat6 | Cat6-rated, staggered load bar, shielded if needed | Supports higher frequencies, check fitment |
| Cat6a | Cat6a-rated, field termination plug, shielded | Thicker cable, requires precise connector match |
| Cat8 | Cat8-rated, shielded, supports 22-24 AWG | For high-speed, short-distance data center use |
RJ45 Plug Compatibility with Solid vs. Stranded Cable
You need to match the RJ45 plug to the type of cable conductor. Solid and stranded cables serve different purposes and require specific plug designs.
- Solid cables use a single copper wire per conductor. These cables work best for long runs inside walls or risers.
- Stranded cables contain multiple thin wires twisted together. These cables provide flexibility and are ideal for short patch cables.
- RJ45 plugs for solid cables have a pin design that pierces the solid conductor for a secure connection.
- RJ45 plugs for stranded cables feature a pin layout that grips the multiple strands, ensuring reliable contact.
- Both shielded and unshielded RJ45 plug options exist for solid and stranded cables.
- Plugs with 2 prongs are designed for stranded cables only. Plugs with 3 prongs can accommodate both stranded and solid conductors.
- Always check the plug’s fitment range for conductor insulation diameter and cable jacket OD. This ensures a snug fit and reliable termination.
Note: Using the wrong RJ45 plug type can lead to poor connections, intermittent network issues, or complete signal loss.
| Cable Type | Recommended RJ45 Plug Type | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Solid | Solid-conductor plug | In-wall, riser, long runs |
| Stranded | Stranded-conductor plug | Patch cables, flexible runs |
| Both | 3-prong universal plug | Mixed environments |
Wire Gauge (AWG) and RJ45 Plug Fit
You must also consider the wire gauge, measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG), when selecting an RJ45 plug. The wire gauge affects both the fit and the performance of your network.
Standard RJ45 plugs support conductor wire gauges from 22 AWG to 28 AWG. Most Cat5e cables use 24-26 AWG, Cat6 and Cat6a cables use 23 AWG, and Cat8 cables use 22-24 AWG. The plug’s design must match the cable’s jacket OD and conductor insulation diameter. For example, a Cat6 cable with 23 AWG solid conductors and a conductor insulation diameter of 0.96mm requires an RJ45 plug that fits these exact specifications.
Thicker wires (lower AWG numbers) offer lower electrical resistance, which improves signal quality over long distances and supports higher power delivery for applications like Power over Ethernet (PoE). Thinner wires (higher AWG numbers) provide more flexibility, making them suitable for short patch cables. Always select an RJ45 plug that matches your cable’s wire gauge and physical dimensions to ensure a secure fit and optimal network performance.
Callout: Matching the RJ45 plug to your cable’s AWG and physical dimensions prevents loose connections, signal loss, and costly rework.
Cable Jacket Diameter and RJ45 Connector Size
You need to pay close attention to the cable jacket diameter when selecting an RJ45 connector. The outside diameter (OD) of your cable determines whether the connector will fit securely and provide a reliable termination. If you choose a connector that is too small, you will struggle to insert the cable, and you risk damaging the insulation. If the connector is too large, the cable may slip out, causing intermittent connectivity or signal loss.
Manufacturers design RJ45 connectors to accommodate specific cable jacket diameters. Most Cat5e and Cat6 cables have a jacket OD between 5.0mm and 6.5mm. Cat6a and Cat8 cables often feature thicker jackets, sometimes exceeding 7.0mm. Always check the technical specifications for both the cable and the connector before making a purchase.
You should also consider the insulation diameter of each conductor inside the cable. Some connectors include load bars or inserts to help align thicker conductors, especially in high-performance cables. These features ensure that each wire seats properly and maintains contact with the connector pins.
Tip: Use a caliper or cable gauge tool to measure your cable’s jacket OD before selecting an RJ45 connector. This step helps you avoid costly mistakes and ensures a snug, professional fit.
A mismatch between cable jacket diameter and connector size can lead to several problems:
- Loose connections that cause network drops
- Difficulty crimping the connector onto the cable
- Exposed conductors that increase the risk of interference
You can refer to the table below for typical cable jacket diameters and recommended RJ45 connector size ranges:
| Cable Category | Typical Jacket OD (mm) | Recommended Connector Size Range (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Cat5e | 5.0 – 6.0 | 5.0 – 6.5 |
| Cat6 | 5.5 – 6.5 | 5.5 – 7.0 |
| Cat6a | 6.5 – 7.5 | 6.5 – 8.0 |
| Cat8 | 7.0 – 8.5 | 7.0 – 8.5 |
Always match the connector size to your cable’s jacket OD for a secure and reliable installation.
Shielding Requirements for RJ45 Plugs
You must evaluate shielding requirements carefully when choosing an RJ45 connector. Shielded cables protect your network from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). To maintain this protection, you need to use shielded RJ45 connectors that match your cable’s construction.
Industry guidelines recommend the following practices:
- Shielded cables require shielded RJ45 connectors to ensure proper grounding and continuous shielding.
- Unshielded cables should use unshielded connectors. Using shielded connectors on unshielded cables does not improve performance and may cause fitment issues or confusion about the cable’s capabilities.
- Focus on physical fitment parameters rather than just the cable category. Consider the cable jacket OD, conductor insulation diameter, conductor type (solid or stranded), and copper AWG gauge.
- Shielded connectors come in two main types: internal ground and external ground. Internal ground connectors work best with thinner shielded Ethernet cables. External ground connectors suit thicker shielded cables with heavy insulation.
Note: Matching connector specifications to your cable’s characteristics ensures both electrical performance and mechanical reliability.
You should always verify that the shielded RJ45 connector you select matches the shielding type and thickness of your cable. This practice prevents signal loss and maintains network integrity in environments with high EMI. If you use an unshielded cable in a low-interference area, an unshielded connector provides a cost-effective and reliable solution.
When you follow these guidelines, you create a robust network infrastructure that resists interference and delivers consistent performance.
Step-by-Step RJ45 Plug Selection Guide
Quick Checklist for RJ45 Plug Compatibility
Before you select the best rj45 connector for your networking project, use this checklist to ensure compatibility and reliability:
- Confirm the cable category (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, Cat8) by checking the sheath.
- Determine if your cable is shielded or unshielded. Use shielded connectors only with shielded cables.
- Match the connector to the conductor type—solid or stranded.
- Check the cable’s outside diameter and conductor insulation diameter for a proper fit.
- Verify the connector supports your required data speed and bandwidth (100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, or higher).
- Ensure the connector meets PoE standards if your applications require power delivery.
- Evaluate if you need rugged or waterproof connectors for harsh environments.
- Confirm the wiring pattern (T568A or T568B) and use it consistently on both ends.
- Inspect the connector for gold-plated pins and robust construction.
- Test all network connections with a cable tester after installation.
Tip: Always source connectors from trusted suppliers and check for compliance with ANSI/TIA-1096-A and IEC 60603-7 standards.
Decision Tree: Which RJ45 Connector Do You Need?
Choosing the right rj45 connector for your applications can seem complex, but a simple decision tree can guide you:
- Is your cable shielded?
- Yes: Select a shielded rj45 connector.
- No: Use an unshielded rj45 connector.
- What is your cable’s conductor type?
- Solid: Choose a connector designed for solid conductors.
- Stranded: Pick a connector for stranded conductors.
- Do you need a pass-through or standard connector?
- Prefer easy verification and quick assembly: Use a pass-through connector.
- Need a compact, durable termination: Use a standard connector.
- Will your applications run in harsh or outdoor environments?
- Yes: Choose ruggedized or waterproof rj45 connectors.
- No: Standard connectors are sufficient.
- Does your network require high data rates or PoE?
- Yes: Ensure the connector supports your speed and power requirements.
This approach helps you select the best rj45 connector for both typical and specialized networking applications.
Real-World RJ45 Plug Selection Examples
You can learn from real-world networking scenarios where improper rj45 selection caused issues. The table below highlights common mistakes and their solutions:
| Scenario Description | Cause | Network Issues | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing facility experienced 20% packet loss | Unterminated shield drains in Cat6A cables | Packet loss, reduced network performance | Implemented proper shielded termination techniques, resulting in 15% productivity boost |
| Excessive untwisting of cable pairs beyond 13mm | Increased crosstalk and noise | Elevated noise levels, reduced signal-to-noise ratio, increased bit error rates | Adhered to industry standards limiting untwisting to 13mm during termination |
| Poor strain relief installation | Mechanical stress on conductor connections | Intermittent connectivity, conductor breakage, difficult-to-diagnose faults | Applied proper strain relief techniques distributing mechanical forces across cable jacket |
| Connector pin misalignment due to incomplete conductor insertion | Incomplete electrical connections | Intermittent failures under load despite initial functional tests | Visual inspection through transparent connectors and re-termination |
| Termination faults causing impedance mismatches | Impedance discontinuities at higher frequencies | Reduced throughput and failure at Gigabit speeds despite 100Mbps support | Precise termination, use of high-quality components, and TDR testing to locate faults |
These examples show that careful rj45 selection and proper installation techniques prevent costly network issues. You can avoid downtime and ensure reliable network connections by following industry standards and using the best rj45 connector for your applications.
Common RJ45 Plug Selection Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Choosing the right RJ45 connector for your Ethernet cable can seem straightforward, but many users make mistakes that compromise network reliability. You can avoid costly errors by understanding the most common pitfalls and following best practices for selecting and installing connectors.
Using the Wrong RJ45 Plug for the Cable Type
You might think any RJ45 connector will work with any Ethernet cable, but this is not the case. Each cable type—Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, or Cat8—has specific requirements for connector fit and performance. If you select a connector based only on the cable’s category label, you risk poor fitment and unreliable connections. For example, using a Cat6 connector on a Cat6a cable with a thicker jacket can cause mechanical instability and signal loss.
Common mistakes include:
- Relying on category labels instead of checking cable jacket diameter and conductor insulation size.
- Mixing connectors and cables from different vendors without verifying physical compatibility.
- Using pass-through connectors on solid copper cables, which can reduce connection reliability.
Tip: Always check the technical specifications for both the cable and the connector. Match the outside diameter and conductor type for a secure fit.
Ignoring Shielding Needs in RJ45 Connectors
Shielding plays a critical role in environments with high electromagnetic interference (EMI). If you ignore shielding requirements, you expose your network to data errors and signal loss. Using unshielded connectors with shielded cables breaks the shield continuity, making your network vulnerable to EMI.
| Scenario | What Happens | Impact on Network |
|---|---|---|
| Use shielded RJ45 connectors with shielded cables | Maintains EMI protection | Stable, error-free data transmission |
| Use unshielded connectors with shielded cables | Breaks shield continuity | Increased EMI, data corruption, signal loss |
| Improper grounding of shield | Shield becomes a source of interference | Network disruptions, higher error rates |
You must ensure proper grounding and shield continuity when installing shielded connectors. In high-EMI environments, such as factories or hospitals, this step preserves data integrity and network performance. If you use shielded connectors in low-EMI environments without proper grounding, you may actually degrade performance.
Note: Always match the shielding type of your cable and connector, and follow grounding best practices to prevent interference.
Overlooking Wire Gauge and Jacket Size Compatibility
You need to pay close attention to wire gauge and jacket size when selecting RJ45 connectors. Mismatching connector dimensions with cable specifications leads to poor fitment and unreliable terminations. If the connector is too large or too small for the cable, you risk mechanical instability, increased crosstalk, and even physical damage.
Problems you may encounter include:
- Unreliable electrical connections that cause intermittent network drops.
- Increased crosstalk and failure to achieve high network speeds.
- Mechanical instability that allows cables to shift or disconnect.
- Damage to conductors if you use connectors not designed for the cable’s wire gauge or type.
You should always use strain relief boots to stabilize the connection and prevent cable shift. Proper selection of RJ45 connectors that match your cable’s wire gauge and jacket size is essential for network reliability.
Callout: Take the time to measure your cable’s jacket diameter and check the connector’s fitment range. This step prevents costly rework and ensures a stable, high-performance network.
Poor RJ45 Plug Installation Practices
You might select the right RJ45 plug, but poor installation practices can still undermine your network’s reliability. Many network issues stem from improper termination, careless crimping, or neglecting essential steps during installation. You need to pay close attention to each stage of the process to ensure a stable and high-performance connection.
Common RJ45 Plug Installation Mistakes:
-
Insufficient Wire Stripping:
If you strip too little insulation, the wires may not seat properly in the connector. Excess insulation can prevent the contacts from piercing the conductor, resulting in intermittent connectivity. -
Excessive Untwisting of Pairs:
Untwisting the wire pairs beyond the recommended length increases crosstalk and signal loss. You should keep the twist as close to the connector as possible—industry standards suggest no more than 13mm. -
Improper Wire Order:
Mixing up the T568A and T568B wiring patterns leads to mismatched pinouts. This mistake causes network failures and makes troubleshooting difficult. -
Weak Crimping Pressure:
If you do not apply enough force with the crimping tool, the contacts may not penetrate the wire insulation. This results in unreliable connections and frequent drops. -
Skipping Cable Testing:
You might assume your installation is correct, but without testing, hidden faults can persist. Always use a cable tester to verify continuity and pinout accuracy.
Tip:
Always double-check the wire order before crimping. A visual inspection can prevent costly rewiring.
Consequences of Poor Installation:
| Mistake | Network Impact | Troubleshooting Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect wire order | No link, slow speeds | High |
| Weak crimping | Intermittent drops | Medium |
| Excessive untwisting | Increased crosstalk, errors | Medium |
| Skipping testing | Hidden faults | High |
You can avoid these problems by following best practices:
- Use a high-quality crimping tool designed for your RJ45 plug type.
- Maintain the correct wire order and minimize untwisting.
- Strip the cable jacket and insulation to the manufacturer’s recommended length.
- Insert wires fully into the connector before crimping.
- Test every cable after termination.
Alert:
Rushing the installation process often leads to costly network downtime. Take your time and follow each step carefully.
You build a reliable network when you combine proper plug selection with disciplined installation techniques. Consistent attention to detail ensures your RJ45 connections deliver optimal performance and long-term durability.
Best Practices for RJ45 Plug Installation
Preparing Ethernet Cable for RJ45 Connector Termination
Proper preparation of your Ethernet cable sets the foundation for reliable network connections. Industry experts recommend a step-by-step approach to ensure you achieve the best results:
- Gather all necessary tools: cable stripper, crimping tool, RJ45 connectors, and a cable tester.
- Strip the outer sheath of the cable carefully. Avoid nicking or damaging the inner wires.
- If you work with Cat6 or Cat6A cables, remove any spline wings. For Cat5e, you can skip this step.
- Untwist the cable pairs gently and straighten the conductors. Take care not to break or kink them.
- Arrange the wires in the correct order according to the T568A or T568B wiring standard.
- Trim the wires evenly to about half an inch from the sheath. Use flush cutters for a clean finish.
- Insert the wires fully into the RJ45 connector, making sure the sequence remains correct and the cable jacket fits snugly into the rear of the plug.
- Push the cable jacket into the connector to secure strain relief and prevent kinks.
- Inspect your work to confirm that all wires are fully seated and in the correct order.
Tip: Double-check the wire order before crimping. A quick visual inspection can prevent costly mistakes later.
Crimping Tips for Reliable RJ45 Connections
Crimping the RJ45 connector correctly is essential for stable and high-performance connections. You should follow these best practices:
- Use a high-quality crimping tool designed for RJ45 connectors. This ensures a secure termination and prevents damage.
- Maintain the correct wire color order throughout your network. Stick to either T568A or T568B for consistency.
- Avoid over-crimping, which can damage the connector and degrade signal quality.
- Choose quality cables and connectors from reputable manufacturers. This reduces the risk of intermittent connectivity issues.
- In harsh or outdoor environments, select weatherproof connectors and shielded cables for added protection.
- After crimping, inspect the connector to ensure the metal contacts have pierced the conductors and the strain latch has engaged.
Note: Consistency in wiring standards across your network is critical for reliable connections and easy troubleshooting.
Testing RJ45 Plug Installations
Testing your RJ45 plug installations verifies that your connections meet performance and reliability standards. You should use a network cable tester, such as the Fluke LinkIQ or similar devices, to check for proper wiring and signal quality. Connect the tester to both ends of the cable and run the test to identify any faults, such as breaks, shorts, or crosstalk. These tools also help you confirm wire mapping and continuity.
Recommended tools for testing include network cable testers, Ethernet testers, and tone generators. Devices like the MicroScanner Cable Verifier or IntelliTone Pro 200 LAN Toner and Probe can help you trace cables and detect faults. Always test each cable after termination to ensure your network connections function as intended.
Callout: Reliable testing ensures your network delivers consistent performance and minimizes downtime due to faulty terminations.
Quick-Reference RJ45 Plug Compatibility Chart
When you select RJ45 plugs for your network, you need a clear overview of compatibility. This quick-reference chart helps you match plugs to cable types, speeds, shielding, and installation needs. You can use this chart to compare connector categories, supported speeds, shielding types, and typical use cases. This approach ensures you choose the right plug for your jacks and avoid costly mistakes.
| Connector Category | Supported Speed | Bandwidth | Shielding Type | Typical Use Case / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat5e | Up to 1 Gbps | 100 MHz | Unshielded (UTP) | Home networking, streaming HD content, compatible with most jacks |
| Cat6 | Up to 10 Gbps* | 250 MHz | Shielded (STP) | High-density setups, 4K streaming, improved EMI protection, fits most jacks |
| Cat7 | Up to 10 Gbps | 600 MHz | Double Shielded (S/FTP) | High-end installations, 4K/8K streaming, excellent interference protection, requires compatible jacks |
*Cat6 supports 10 Gbps over short distances (up to 55 meters).

You should always check the physical fitment of your plugs with your jacks. Cable outer diameter, conductor insulation diameter, and conductor type (solid or stranded) all affect compatibility. If you use jacks that do not match your plug’s dimensions, you risk unreliable connections. Many installers overlook the importance of matching plug and jack dimensions, especially when working with rj45 keystone jacks in patch panels or wall plates.
Shielding type also plays a key role. You must pair shielded plugs with shielded cables and shielded jacks to maintain EMI protection. Unshielded plugs work best with unshielded cables and standard jacks in low-interference environments. Double-shielded plugs, such as those for Cat7, require jacks that support advanced shielding and grounding.
When you install rj45 keystone jacks, you need to confirm that your plugs fit securely and support the required bandwidth. Some legacy jacks may not accommodate newer, thicker plugs, especially for Cat6a or Cat7. Always review manufacturer specifications for both plugs and jacks. This step prevents installation issues and ensures your network meets performance standards.
You should also consider installation factors. Some plugs offer easier crimping or better strain relief, which helps when you terminate cables into jacks or rj45 keystone jacks. If you work with high-density racks, compact plugs and jacks save space and simplify cable management.
Note: Always match your RJ45 plug, cable, and jacks for optimal performance. This practice reduces troubleshooting time and improves network reliability.
A quick checklist for using this chart:
- Identify your cable category and shielding needs.
- Confirm plug fitment with your jacks, including rj45 keystone jacks.
- Check supported speed and bandwidth for your application.
- Review installation requirements for your jacks and plugs.
This chart gives you a fast, reliable way to select the right RJ45 plug for your network. You can avoid common pitfalls and ensure every connection in your jacks and rj45 keystone jacks delivers the performance you expect.
You can ensure reliable network performance by following smart RJ45 plug selection practices.
- Always match rj45 connectors to your cable category and environment.
- Use shielded rj45 in high-EMI areas and unshielded rj45 for typical office or home setups.
- Select ruggedized rj45 for harsh conditions and confirm your jacks support the chosen plug.
- Double-check compatibility between rj45, jacks, and cable type to prevent fitment or signal issues.
- Inspect jacks for wear and replace damaged ones with high-quality rj45.
- Use the checklist and compatibility chart to verify that your rj45, jacks, and rj45 connectors meet your network’s needs.
- Properly installed rj45 and jacks reduce troubleshooting and keep your network stable.
- Consistent attention to jacks and rj45 selection supports long-term performance.
- Plan your rj45 and jacks for both current and future bandwidth requirements.
- Reliable jacks and rj45 choices help you avoid costly downtime.
Tip: Systematically review your rj45, jacks, and rj45 connectors before purchase. This step ensures you achieve the best results for every network installation.
FAQ
What is the difference between RJ45 plugs and jacks?
You use RJ45 plugs to terminate Ethernet cables. You install jacks in wall plates, patch panels, or devices. Plugs connect to jacks, creating a secure network link. Both must match in category and shielding for reliable performance.
Can I use Cat6 plugs with Cat5e jacks?
You can connect Cat6 plugs to Cat5e jacks, but you limit your network speed to Cat5e performance. For best results, match the plug and jack category. This ensures you achieve the highest supported speed and signal quality.
How do I know if my jacks are shielded?
You can identify shielded jacks by their metal housing and grounding tab. These features help block electromagnetic interference. Always pair shielded plugs with shielded jacks to maintain network protection in high-interference environments.
Do all RJ45 jacks support Power over Ethernet (PoE)?
Most modern jacks support PoE, but you should check the product specifications. If you plan to use PoE devices, confirm that both the jacks and plugs meet the required standard for safe power delivery.
Can I reuse RJ45 plugs or jacks after removal?
You should not reuse RJ45 plugs. Crimping damages the contacts, which can cause unreliable connections if reused. You can sometimes reuse jacks, but only if they remain undamaged and clean after removal.
What tools do I need to install RJ45 plugs and jacks?
You need a cable stripper, crimping tool, and cable tester for plugs. For jacks, use a punch-down tool. Always test your connections after installation to ensure proper wiring and performance.
How do I choose the right jack for my network?
Select jacks that match your cable category, shielding needs, and installation environment. For high-speed or PoE networks, choose jacks rated for those features. Review manufacturer specifications to ensure compatibility with your plugs and cables.
Tip: Always test your network after installing new plugs or jacks. This step helps you catch wiring errors before they cause problems.




